Are Chinese EV cars reliable

China's EV market is exploding here are 5 major Chinese car brands you should know
Zeekr is an electric vehicle brand under the privately held Chinese auto giant Geely which boughtthe Swedish brand Volvo in 2010.
Founded only in 2021, Zeeker already has international ambitions.
In April this year, Zeekr said it plans to sell its newly launched SUV-style Zeekr X and Zeekr 001 EV sedan in Western Europe, Reuters reported. The EV maker did not indicate a timeline for its plans.
The $27,000 Zeekr X even has facial recognition software to unlock the car and owners can also opt to install a refrigerator in the car, Andy An, the CEO of Zeekr, said at an event, Reuters further reported.
The company aims to deliver 40,000 Zeekr X cars to the China market this year, with its first domestic deliveries starting in June, An said per Reuters.
And even though Zeekr is backed by a major auto player, it still trails its EV peers in the domestic Chinese markets.
Zeekr sold just 15,234 of its existing models in the first quarter of 2023 this is half of the 31,000 vehicles Nio sold and just 10% of what Tesla sold in the same period, per Reuters.
Heres what you need to know about BYD, the Chinese EV giant that just overtook Tesla
Editors Note: Sign up for CNNs Meanwhile in China newsletter, which explores what you need to know about the countrys rise and how it impacts the world.
Hong KongCNN
BYD overtook Tesla as the worlds top seller of electric vehicles (EV) at the end of last year, crowning an extraordinary rise for the Chinese carmaker.
It delivered more fully electric cars than Tesla for the first time in the three-month period to December 31, and slashed the sales lead held by Elon Musks company over the year as a whole.
So how did a little-known Chinese battery maker grow so quickly to become Teslas biggest rival?
Based in the Chinese megacity of Shenzhen, BYD was founded in 1995 by Wang Chuanfu, a low-key former academic who still runs the company. Wang says the letters BYD dont stand for anything in particular. He said he chose a rather strange name to set it apart from other startups.
It is Chinas top EV producer and exports electric taxis, buses and other vehicles to the rest of the world, including Europe, South America, Southeast Asia and the Middle East. Unlike Tesla (TSLA), it also makes plug-in hybrids.
Israel and Thailand currently countas BYDs major overseas markets, where the Chinese company ranks number one in EV sales.
Its best-selling passenger cars are the Qin and Song models. The Qin is a compact sedan available as a plug-in hybrid or an all-electric car. The BYD Song is a series of compact crossover SUVs.
Compared to Tesla, BYD is known for offering more affordable cars, which helped it attract a wider group of consumers. Its entry-level model sells in China for just over $10,000; the cheapest Tesla Model 3 costs more than $32,000.
BYDs passenger cars are not yet available in the United States. But its electric buses made in Lancaster, California are soldin the country.
Wang, an engineer, first moved to Shenzhen in the early 1990s to run a battery making business for a Beijing-based government research institute, according to his official resume in the companys filings.
Government posts in China at that time were considered iron rice bowls, a popular term for a job for life.But Wang soon quit and founded BYD.
The start of his entrepreneurial journey coincided with the opening of the Chinese economy to the world. Chinas former leader Deng Xiaoping had set up the countrys first special economic zone in Shenzhen, which encouraged hundreds of manufacturing businesses to flock to the city, lured by its liberal economic policies and cheaper labor and land costs.
By 1997, Wang had grown his small workshop to a medium-sized cellphone battery maker with more than 100 million yuan ($14 million) in annual sales.
That year, the Asian financial crisis provided a growth opportunity as plunging battery prices pushed many competitorsout of business. Wangs company was ableto survive due to its cost advantage, according to the Southern Weekly newspaper.
By 2003, BYD had become the worlds largest producer of nickel-cadmium batteries, which were widely used in mobile phones.
But Wang wanted more. Eyeing the future growth of EVs, Wang ventured into the car industry in 2003, acquiring a state-owned automaker in the city of Xian for269 million yuan ($38 million).
While that surprise decision angered the companys strategic investors and triggered a 21% plunge in the companys Hong Kong-listed shares, as Wang later described, he remained steadfast.
I build cars because I am optimistic about the future development of electric vehicles, he said defiantly after the share price plunge, according to state-owned Beijing Business Today.
Just five years later, in 2008, Wang was vindicated when he received a $230 million investment from his most famous backer, Warren Buffett, who paid about $1 per share for a stake of around 10%. That vote of confidence helped boost the companys stock by as much as 1,370% over the next year.
BYD launched its first plug-in hybrid model at the end of 2008. Since then, BYD has taken off as an EV manufacturer, partly thanks to the Chinese governments support for the industry.
Buffett has been gradually trimming his stake in BYD since 2022, taking some of the enormous profits he has made. According to the most recent filing by Buffetts Berkshire Hathaway, the firm held nearly 8% of BYD as oflate October. Those shares are now worth 18.28 billion Hong Kong dollars ($2.3 billion).
BYD has dominated the Chinese EVindustry since 2015, when it surpassed its domestic and overseas rivals in the worlds biggest car market. One of its key advantages against Tesla, the number two player in China, is price.
Teslas four models the Model 3, Model Y, Model S and Model X have price tags ranging from $40,000 to $120,000 in the United States.In China, the cheapest Tesla model, the base Model 3,has a starting price of 229,900 yuan ($32,375). It has a range of 272 miles on a full charge and a top speed of 140 miles per hour.
By contrast, the BYD Seagull has a starting price of 73,800 yuan ($10,392) in China. It has a top speed of 81 miles per hour.The Seagull is available with two battery packs.The smaller battery has a range of 190 miles, while the larger battery has a range of 251 miles.
Both Tesla and BYD vehicles have received safety ratings from international organizations. In 2022, Teslas Model Y and BYDs Atto 3 received a five-star Australasian New Car Assessment Program (ANCAP) rating respectively.
Since 2020, BYD has been making its lithium iron phosphate battery (LFP) Blade Batteries for usein its own cars and for sale to other auto makers, such as Toyota.
The companysaysthe blade-shaped battery is thinner and longer than conventional lithium iron cells, and thus can maximize the use of available space within the battery pack. Its also less likely to catch fire even when its severely damaged, according to BYD.
Tesla also reportedly uses BYD Blade Batteries for its Y cars produced in the Berlin Gigafactory, according to German media.
In March 2023, Elon Musk denied a media report saying Tesla was ending cooperation with BYD on battery supply.
Chinese Electric Cars: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
China is the worlds largest market for electric vehicles, and Chinese brands are increasingly making their mark on the global stage. But what are the pros and cons of Chinese electric cars?
Chinese Electric Cars: A Pros and Cons Analysis
Overall, Chinese electric cars offer a number of advantages, including low cost, good range, and advanced technology. However, there are still some concerns about their reputation and safety. As the quality of Chinese electric cars continues to improve, and the charging infrastructure becomes more widespread, these concerns are likely to diminish.
Chinese electric cars have a number of pros and cons, which are summarized below:
Pros:
- Affordability:Chinese EV cars are often very affordable, making them a good option for budget-minded buyers.
- Technology:Chinese automakers are investing heavily in electric vehicle technology, and some of their cars offer cutting-edge features.
- Performance:Chinese electric cars are often very efficient and have impressive range.
- Design:Chinese automakers are becoming more sophisticated in their design, and their cars are starting to look more like their European and American counterparts.
Cons:
- Quality:Some Chinese electric cars have been criticized for their quality, with reports of poor build quality and reliability issues.
- Range:The range of some Chinese EV cars is still not as good as that of their European and American counterparts.
- Charging infrastructure:The charging infrastructure in China is not as developed as in some other countries, which can make it difficult to find places to charge your car.
- Safety:There have been some concerns about the safety of Chinese electric cars, with reports of fires and other incidents.
- Intellectual property theft:Chinese automakers have been accused of intellectual property theft, which could have implications for the long-term sustainability of the Chinese electric vehicle industry.
Conclusion
Chinese electric cars offer a lot of potential, but there are still some concerns about quality, range, and safety. As the Chinese electric vehicle industry continues to develop, it will be interesting to see how these issues are addressed.
Why Are Chinese Electric Vehicles (EVs) So Cheap?
China is the worlds leading producer of electric vehicles (EVs), and the prices of Chinese EVs are significantly lower than those of EVs from other countries. There are a number of factors that contribute to the lower cost of Chinese EVs, including:
- Government subsidies:The Chinese government provides significant subsidies to EV manufacturers, which helps to keep the cost of EVs down.
- Economies of scale:China has a large and growing market for EVs, which allows EV manufacturers to benefit from economies of scale.
- Lower labor costs:Labor costs in China are lower than in many other countries, which helps to keep the cost of EV manufacturing down.
- Access to raw materials:China has access to a large supply of the raw materials used in EV batteries, such as lithium and cobalt. This gives Chinese EV manufacturers a cost advantage over manufacturers in other countries.
- Government regulations:The Chinese government has implemented a number of regulations that are designed to promote the development of the EV industry. These regulations include requirements for automakers to produce a certain number of EVs each year and for charging stations to be installed in public places.
As a result of these factors, Chinese EVs are typically 20-30% cheaper than EVs from other countries. This has made Chinese EVs more affordable for consumers, and it has also helped to boost the global adoption of EVs.
The Future of Chinese EVs
The Chinese EV market is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. As the cost of EVs continues to fall, more and more consumers will be able to afford to buy them. This will help to accelerate the transition to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation system.
In addition, the Chinese government is committed to promoting the development of the EV industry. The government has set a goal of having 100 million EVs on the road by 2030. This will require a significant increase in the production of EVs, and it is likely that Chinese EV manufacturers will continue to play a leading role in this market.
Conclusion
Chinese EVs are so cheap for a number of reasons, including government subsidies, economies of scale, lower labor costs, access to raw materials, and government regulations. The Chinese EV market is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, and Chinese EV manufacturers are likely to play a leading role in this market.
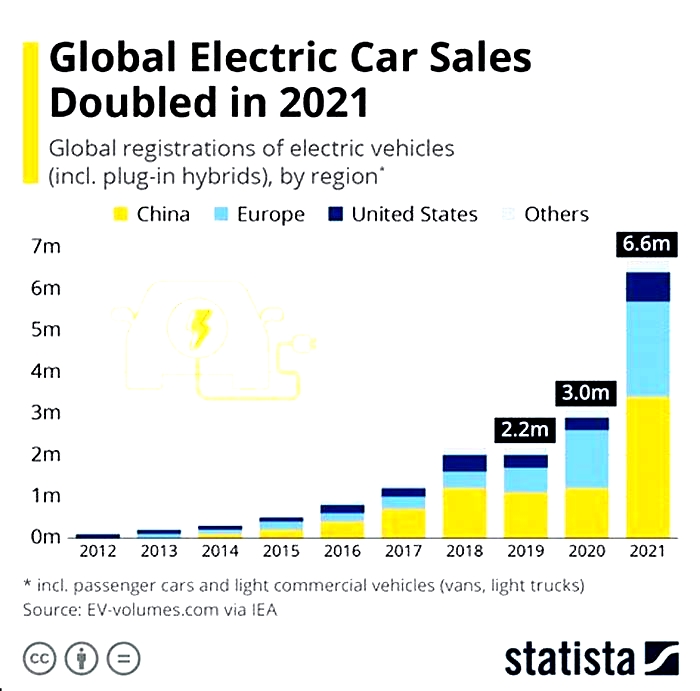
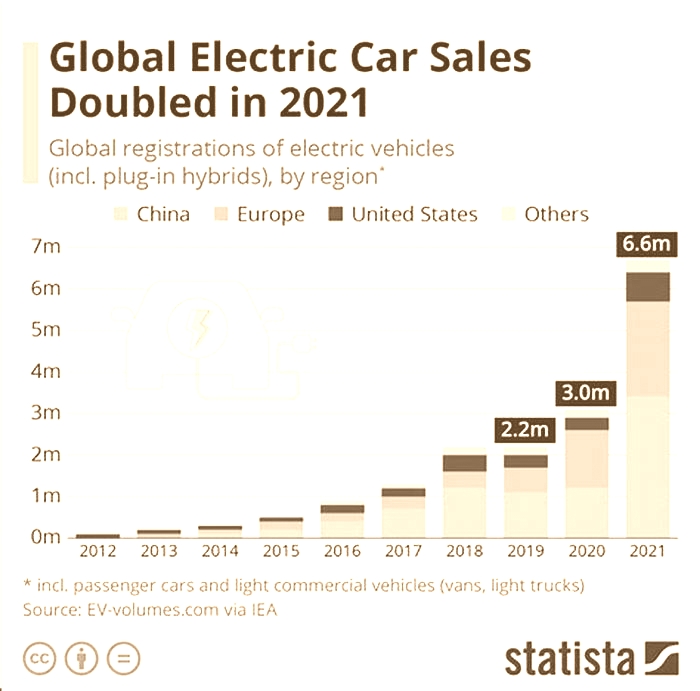
Chinas EV Market Is Exploding
The electric vehicle (EV) market is exploding in China, and for good reason. The country has a number of factors that make it a natural leader in the EV space, including:
- Government support: Chinas government has been aggressively promoting the development of EVs, providing subsidies and other incentives to manufacturers and consumers.
- A large and growing market: China has the worlds largest auto market, and the demand for EVs is growing rapidly.
- A competitive EV ecosystem: China has a number of strong EV manufacturers, as well as a well-developed supply chain for EV components.
As a result of these factors, Chinas EV market is now the largest in the world. In 2022, China sold over 5.5 million EVs, accounting for more than half of global EV sales. And the market is only going to get bigger in the years to come.
Who Are the Top Chinese Electric Cars Makers in China?
There are a number of Chinese EV makers that are leading the charge in the global EV market. Some of the most notable include:
- BYD: BYD is the largest EV maker in China, and the second-largest in the world. The company sells a wide range of EVs, including sedans, SUVs, and buses.
- NIO: NIO is a luxury EV maker that is known for its high-performance vehicles. The companys cars are popular among young Chinese consumers.
- Xpeng: Xpeng is another luxury EV maker that is gaining popularity in China. The companys cars are known for their advanced features and technology.
- GAC Aion: GAC Aion is a subsidiary of Guangzhou Automobile Group (GAC) that specializes in EVs. The companys cars are known for their affordability and long range.
- SAIC-GM-Wuling: SAIC-GM-Wuling is a joint venture between SAIC Motor, General Motors, and Wuling Motors. The companys Hongguang Mini EV is the best-selling EV in China.
What Are the Challenges Facing Chinas EV Market?
While Chinas EV market is booming, there are still some challenges that the country needs to address. These include:
- The high cost of EVs: EVs are still more expensive than traditional gasoline-powered cars. This is a barrier to entry for many consumers.
- The lack of charging infrastructure: China still has a relatively underdeveloped charging infrastructure. This makes it difficult for EV owners to travel long distances.
- The lack of consumer awareness: Many Chinese consumers are still not aware of the benefits of EVs. This is a challenge that the government and EV makers need to address.
Despite these challenges, Chinas EV market is poised for continued growth in the years to come. The country has the resources and the commitment to make EVs a major part of its transportation future.
What Does the Future Hold for Chinas EV Market?
The future of Chinas EV market is very bright. The country is well-positioned to become a global leader in the EV space. In the years to come, we can expect to see even more growth in the Chinese EV market, as well as the development of new and innovative EV technologies.
Chinas EV market is a major driver of global EV growth. As the country continues to invest in EVs, it will have a significant impact on the future of the global transportation sector.