Can an EV battery last 20 years
What is the lifespan of an electric car battery?
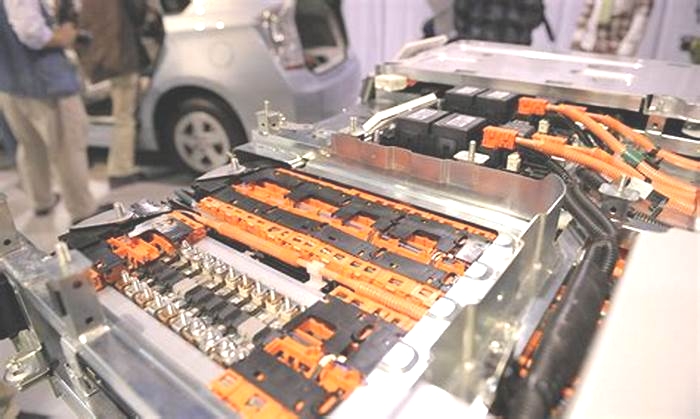
Most car manufacturers guarantee EV batteries for eight years/160,000km, with some estimates suggesting electric car battery life is somewhere between 10 and 20 years. Electric vehicle (EV) batteries can also be replaced if required.
As the most expensive part of an EV, youd hope that the lithium-ion batteries contained in the cars battery pack would last significantly longer than, say, Kanye Wests Presidential run, or defunct streaming platform Quibi (if you dont know what that is, consider our point made).
When it comes to EVs, if youre wondering How long do car batteries last?, Australia has several car manufacturers - including Tesla, Audi, Mercedes-Benz, BMW and Nissan - that guarantee EV batteries for eight years or 160,000km, whichever comes first (most guarantees state that the battery should still be holding at least 70 per cent capacity after eight years).
Read more about electric cars
This tracks with the general consensus that EV batteries last for between 10 and 20 years (the battery in a standard internal-combustion engine vehicle lasts between three and five years), although its likely to be closer to the lower end of the spectrum, with the performance of EV batteries being expected to progressively diminish once they hit the decade mark.
This shouldnt come as too much of a shock (pun not intended). As anyone who has a laptop or phone (ie pretty much everyone) knows, the batteries in these items struggle to hold a charge and become less effective once they start getting on a bit in age.
The lifespan and longevity of EV batteries will only get better with time as new technological advancements are made, although there are certain things you can do to ensure your EV battery doesnt fritz out prematurely.
What factors determine the lifespan of a battery?
Download the EVGuide Report, 2022
Australia's one-stop snapshot of all things relating to electric cars.
Download for free
 A rapid charge creates a lot of heat, which can cause battery degradation.
A rapid charge creates a lot of heat, which can cause battery degradation.
The answer to the question How long do electric cars last? can be largely answered by However long the battery lasts, and if the battery is exposed to extreme hot or cold temperatures, dont expect that to be as long as youd like.
EV batteries will begin to degrade if the temperature is below zero degrees Celsius or above 27 degrees Celsius, so anything between that range is preferable (unlike some EVs, Tesla carshave a thermal-management system for battery packs, meaning theyll last longer, charge quicker and have higher performance).
Using a DC rapid charger is good if youre in a hurry, but it isnt such a great idea so do so regularly, as a rapid charge that gives you approximately 80 per cent capacity in around 20 to 30 minutes creates a lot of heat, which can cause battery degradation.
Draining an EV battery empty or charging to 100 per cent regularly also puts strain on the battery and causes degradation, so its a good idea to aim to have your EV charged somewhere between 20 per cent and 80 per cent under normal circumstances (a full charge on a long trip, of course, is completely understandable, and driving around on 20 per cent really is for gamblers and risk takers).
The above also applies if you plan on parking the EV for a long period of time: aim for a charge between 20 to 80 per cent, and never leave it fully charged or fully drained.
The only exception to this rule is EVs that use lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, like the Tesla Model 3 and Model Y, as the chemistry used in LFPs isnt affected by states of high or low charge.
How do you know when your EV battery is dying?

 Like an old phone or laptop, an EV battery may struggle to hold charge over time.
Like an old phone or laptop, an EV battery may struggle to hold charge over time.
Although simple ageing will cause an EV batterys ability to hold a charge to degrade over time, its unlikely that the battery pack will stop working altogether - like an old mobile phone or laptop, they may just struggle to hold a charge for any length of time.
What youll notice, then, is that you need to recharge more often, and those charges wont last for as long as youre used to.
While a lot of people might choose to buy themselves a new car after holding onto one for a decade or so, there are options if youve become attached to your EV.
Can you replace an EV battery?

 A Melbourne-based firm will commence a scalable hybrid battery remanufacturing exchange program.
A Melbourne-based firm will commence a scalable hybrid battery remanufacturing exchange program.
Yep, you sure can. It might be that your EV never needs its battery replaced, but if it does, it wont happen until at least a decade into the cars life, at the earliest.
Dealers can replace EV batteries, and prices vary depending on the size of said batteries.
Battery recycling is also slowly becoming a thing, with Toyota, for example, offering a credit toward the price of a new battery for any used EV batteries that are returned for recycling. BMW also has plans to re-purpose old EV batteries for mass power storage or recycling.
Again, though, this may never be necessary, with batteries possibly lasting for a couple of decades, and battery technology developing in the direction where EV batteries will last even longer - and, crucially, take you even further.
EV Lifespan: Do They Last as Long as Gasoline Cars?
Just as gasoline and diesel engines were once new technology and poo-pooed by the horse-driven public, modern battery electric vehicles (EV) are facing the same criticisms. Will electric vehicles be on the road as long as gasoline cars and diesel vehicles? Absolutely, and automakers are already delivering.
Myth Busted: Neither EVs nor Gasoline Cars Are Infallible
Since the first automobile went from production to daily driver to a cube at the junkyard, car and truck lifespan has been increasing. Notwithstanding a few outliers, such as Irv Gordons 3.2-million-mile 1966 Volvo P1800S and Matt Farahs million-mile 1996 Lexus LS400, the increasing life of the typical car is encouraging. In 1977, the average American car was just 5.5 years old. By 1995, it was 8.4 years, and in 2020, the average reached 11.9 years.
That says a lot about todays typical driver expectations and the technical advances implemented to meet them: People want cars that last. EV or gasoline-powered, they expect any car they buy today to be safe, efficient, and reliable years down the road.
Still, where and how any vehicle is driven and maintained has a significant impact on lifespan, regardless of how well an auto might be built. Harsh driving, overloading, corrosion, and neglect will destroy any vehicle before its prime, but well-maintained vehicles are no longer considered worn-out until theyve reached at least 150,000 miles.
No vehicle is infallible but there are some things that tend to give EVs a better shot at a longer lifespan.
EV Key Component Life Expectancy
When youre trying to decide between buying an electric vehicle or a conventional vehicle, there are several shared components to take out of the lifespan comparison. Both types include the following similarities:
- Modern vehicle frame and body construction last the life of the vehicle, depending on environmental factors.
- Electrical systems, such as the radio, navigation system, headlights, taillights, and power windows, generally last upwards of 10 years.
- Steering and suspension components typically last 6 to 10 years.
- Tires generally last 4 or 5 years, depending on driving habits and alignment maintenance.
- Wipers and cabin filters are typically replaced every 6 to 12 months, depending on environmental factors.
- The 12-V battery is also the same, lasting typically 5 to 7 years in typical driving.
- Brake hydraulics and calipers are the same, typically requiring service every other year.
On the other hand, major differences do exist between conventional vehicles and electric vehicles. While modern conventional powertrains, with proper maintenance, are proven to last, electric vehicle batteries and motors arent often given a fair look, mostly because of the expense of critical components like batteries.
Even so, major electric vehicle components are at least as good as their gasoline-chugging counterparts.
Motor
monkeybusinessimages/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Electric motors typically have a single moving part, in comparison to several hundred parts in an engine. Electric motor maintenance is limited to coolant changes every 100,000 miles. Engines, in addition to coolant, require regular oil changes, air filters, and likely spark plugs in that time. Both motors and engines are proven to last upwards of 20 years.
Transmission
da-kuk/Getty images
Since electric vehicles usually arent equipped with a transmission, just a single gear reduction, theyre the clear winner in the transmission lifespan comparison. For modern conventional vehicles, manual and automatic transmissions typically last upwards of 15 years, requiring fluid services at least every 100,000 miles.
Battery
Tesla
Lithium-ion battery packs are expensive, but they last a long time. So far, the typical EV battery has been proven to last about 200,000 miles, nearly 20 years. Tesla is rumored to be developing an EV battery that will last 1,000,000 miles, much longer than the average vehicle, currently 11.9 years. Major EV makers report few battery replacements in the last decade.
Brakes
Brake services offer an interesting comparison. Because electric vehicles use regenerative braking to slow the vehicle, the hydraulic brake system isnt used as much. While conventional vehicle brakes last 25,000 to 65,000 miles, depending on vehicle type and driver habits, hybrid and EV pads and rotors are known to last much longer. Some hybrid and EV owners report their brakes lasting over 100,000 miles.
EV Maintenance Matters!
Electric vehicles simpler powertrains require less service, which actually makes required services more critical. How you drive, charge, and maintain your electric vehicle will play a big part in how long it lasts, just like it does with a gasoline-powered vehicle. There are two key areas to pay attention to.
Cooling System Checks
Cooling system maintenance is important. A combination of active and passive heating and cooling keep the battery pack around 70 F for best lifespan. Pay close attention to cooling system maintenance, such as coolant or air filter replacement.
Battery Charging Practices
Charging practices are critical. While the battery management system (BMS) manages charge rates to protect the battery, you can do your part by charging mainly on Level 2 chargers. You can use Level 3 charging stations on trips, but regular consistent usage of these high-power chargers will impact battery life.
EV Life Expectancy Is at Least Equal to Gas Cars
Given technological advances in both conventional and electric vehicles in the last decade, neither seems to have longevity issues. With responsible driving and maintenance habits, both should last at least a decade, if not much longer.
Government and automaker confidence seems to reflect the desire, if not the reality, of EV longevity. To help encourage confidence in EVs, federal rules now require automakers to cover major components, like the battery and electric motor, for eight years or 100,000 miles, while California extends that to 10 years or 150,000 miles. Some EV automakers even offer a lifetime guarantee, something practically unheard of in conventional vehicle warranties.
If youre shopping for a new vehicle, its good to know you can choose any car that suits you best. Eventually, as pricing and availability become more competitive, its likely that not choosing an electric vehicle will seem like a risky bet.
CarBuzz
Whether they arise from anti-EV lobbyists or permeate through a case of broken telephone, there are plenty of myths surrounding electric vehicles. While some have been dispelled, like how long a battery might last if you're trapped in a snowstorm, many misnomers still exist, and plenty of them pertain to battery charging and operation. Technology has come a long way since the advent of the EV, and with battery tech rapidly evolving, it pays to stay abreast of the current trends and requirements when it comes to getting the most out of your electric vehicle. When battery life and range are crucial aspects of vehicle ownership, you want to make sure that the claims you buy into remain true for years to come. This requires proper care - and charging habits - of your electric vehicle and its battery.
1. Avoid Extreme Temperatures
Batteries rely on the chemical bonds and reactions between the elements inside them. Modern Lithium-ion batteries have vastly improved the range of temperatures at which they can operate, but ideally, you want to avoid extremes. This pertains to both extreme heat and extreme cold, as either has the potential to reduce battery life in the long run at an expedited rate. On hot summer days, park in the shade or under cover. Likewise, don't park outside in a snow storm where you can help it. Parking in a garage is the best bet, but even under a carport to keep the car away from the worst of the cold will help prolong your battery's lifespan.
When you can't manage that, plugging the car in to charge will mitigate problems, as the battery's thermal management systems will manage things for you, keeping the battery at the right temperature.
2. Ease Up On The 0-60 Runs
The modern EV's biggest party trick is acceleration. With instant torque at any speed, even commuter-oriented EVs are capable of outrunning V8-powered sports cars to 60 mph. But rapidly expelling energy repeatedly isn't good for the battery. Modern management systems can mitigate most of the damage, but if you're engaging launch control at every traffic light and discharging the battery at a rapid rate, it'll affect the longevity of the battery and reduce its range prematurely. We're not being the fun police, though, and occasional pulls are fine, but there's a reason a certain tartan-adjacent EV super-sedan takes nearly 10 minutes to prime itself for a sub-10-second -mile run - batteries don't like it.
3. Use A Slow Charger When You Can
Just like EV batteries don't like being discharged rapidly, they don't like being recharged too rapidly either. Modern EVs are touted as being more convenient than ever because of fast-charging capabilities, but just because you can doesn't mean you always should. Drinking a Red Bull might give you a boost now, but drinking three a day for a week straight instead of sleeping properly will wreck you. The same applies to batteries. Unless you need the quick boost part-way through a long road trip or because you unexpectedly need to cover more mileage in a day than planned, a slow home charge prolongs battery life, placing less stress on the battery cells and making sure they don't burn out prematurely. Fast charging is OK on occasion, but not the best thing to make a habit of.
4. Dont Charge Up To 100%
It seems counterintuitive; 100% charge is good, right? A full battery can't be bad, right? Well, yes and no. A full battery is great when you're planning a long-distance journey, as that full top-up can often add 20% distance to your total tally, but repeatedly charging to capacity places strain on the chemical bonds, weakening them over time. Draining a battery fully and recharging from scratch is even worse, damaging the cells substantially more, so while a 100% charge isn't a terrible thing, running your battery down completely is even more likely to reduce your battery's lifespan. The ideal range to keep your battery in is 20-80%. With time, this will likely change as battery and charge management systems evolve, trickle-charging the last little bit so as to avoid unnecessary damage, but for the time being, keeping your battery in the middle 60% of its state of charge will prolong its life substantially.
Many EVs can be set to stop charging at a certain state of charge (SOC). This is a helpful tool in maintaining the battery, and one that can be used for vehicles that spend a lot of their life parked and only get driven once or twice a week.