Do hybrid cars have a future
MIT Technology Review
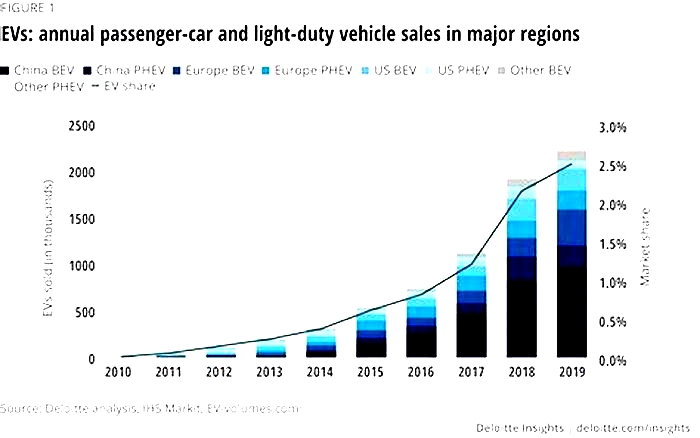
Several major car companies, including GM and Volvo, have announced plans to produce only electric cars by or before 2035, in anticipation of the transition. But not all automakers are on the same page.
Notably, Toyota, the worlds largest automaker, has emphasized that it plans to offer a range of options, including hydrogen-fuel-cell vehicles, instead of focusing exclusively on electric vehicles. A Toyota spokesperson told MIT Technology Review that the company is focused on how to reduce carbon emissions most quickly, rather than how many vehicles of a certain type it can sell.
The company has continued releasing new hybrid vehicles, including plug-in hybrids that can drive short distances on electricity using a small battery. In November, Toyota announced the 2023 edition of its Prius Prime, a plug-in hybrid.
Some environmental groups have criticized the companys slow approach to EVs. To get to zero emissions, they argue, we will need all-electric vehicles, and the sooner the better.
But in recent interviews, Toyota CEO Akio Toyoda has raised doubts about just how fast the auto industry can pull a U-turn on fossil fuels, calling the US target of making EVs reach half of new car sales by 2030 a tough ask. While Toyota plans for EV sales to reach 3.5 million by 2030 (or 35% of its current annual sales), the company also sees hybrids as an affordable option customers will want, and one that can play a key role in cutting emissions.
A tale of two hybrids
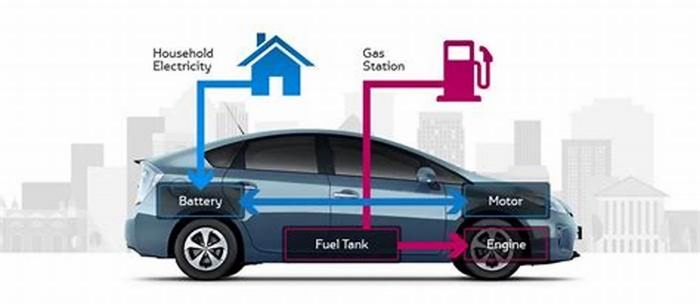
Two different categories of vehicles are referred to as hybrids. Conventional hybrid electric vehicles have a small battery that helps the gas-powered engine by recapturing energy during driving, like the energy that would otherwise be lost during braking. They cannot drive more than a couple of miles on battery power, and slowly at that. Rather, the battery helps boost gas mileage and can provide extra torque. The original Toyota Prius models are among the most familiar traditional hybrid vehicles.
Plug-in hybrid vehicles, on the other hand, have a battery about 10 times larger than the one in a traditional hybrid, and that battery can be plugged in and charged using electricity. Plug-in hybrids can typically run 25 to 50 miles on electricity, switching over to their gasoline engine for longer distances. The Prius Prime, introduced in 2012, is a plug-in hybrid.
Conventional hybrids are far more common in the US than either all-electric or plug-in hybrid vehicles, though sales of electric vehicles have grown quickly over the past several years.
Do Hybrid Cars Have Alternators? Unveiling the Truth!
Hey there, car enthusiasts! Curious about the inner workings of hybrid cars? Well, lets dive into a shocking revelation alternators! These little powerhouses, like the Prius, play a vital role in generating electricity for these eco-friendly vehicles. They may experience alternator problems or issues with starters, which can be resolved by changing them.
Now, you might be thinking, What on earth is an alternator? Dont worry; its not some alien gadget from another galaxy. Its actually an essential component of the electric engine in your Prius. If youre experiencing a problem with your electric starters, the alternator could be the culprit.
Think of it as the Prius starters trusty sidekick, working behind the scenes to recharge the battery and power all those fancy electrical systems in your hybrid car. If youre experiencing an alternator problem, please reply for assistance.
Understanding how alternators and electric starters fit into the grand scheme of things is key to comprehending how hybrid cars with electric engines like the Prius zip around town so efficiently.
Can you please reply to this message? Its like having your very own superhero silently save the day by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
So buckle up (oops, sorry!), because were about to embark on an electrifying journey through the world of alternators and their crucial role in making hybrid cars go vroom while reducing our carbon footprint!
Understanding Alternators and Their Functionality
Alternators are crucial components in hybrid cars as they play a vital role in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. In addition, alternators are responsible for charging the battery and powering the electrical systems of the vehicle.
Without a functioning alternator, the battery would quickly drain and the car would not be able to operate. Therefore, it is important to regularly maintain and service the alternator to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
If you have any questions or need further information about alternators, please feel free to reply to this blog post. Working alongside the engine, alternators generate electricity while the car is running.
This electricity serves two main purposes: charging the battery and supplying power to various components within the vehicle.
Alternators: Powerhouses of Electrical Energy
An alternators primary function is to produce electrical energy that keeps the cars battery charged and ensures smooth operation of electrical systems. As the engine runs, it drives a belt connected to the alternator.
This serpentine belt spins the electric engines alternators rotor inside a stator, creating an electromagnetic field.
Generating Electricity on the Go
The spinning rotor within the stator induces an alternating current (AC) in the windings of the electric engine. The AC produced by this process is then converted into direct current (DC) by a rectifier bridge within the alternator.
The DC output from the rectifier bridge is used to charge the cars battery and power various electrical components such as lights, radio, air conditioning, and more.
Ensuring Optimal Performance
Hybrid cars rely heavily on their electrical systems for smooth functioning. Therefore, it is crucial for alternators to operate efficiently at all times.
However, like any other component in a vehicle, alternators can experience problems over time:
- Alternator Problems: Common issues with alternators include worn-out brushes or bearings, faulty diodes in the rectifier bridge, or damaged wiring connections. These problems can lead to insufficient charging of the battery or even complete failure of electrical systems.
- Signs of Alternator Issues: Drivers should be aware of warning signs indicating potential alternator problems. These signs may include dimming headlights or interior lights when idling or accelerating slowly, frequent dead batteries despite regular recharging, strange noises coming from the alternator, or the battery warning light illuminating the dashboard.
The Importance of Regular Maintenance
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of alternators in hybrid cars, regular maintenance is essential. Here are a few tips to keep your alternator in good shape:
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect the condition of the serpentine belt that drives the alternator. Look for signs of wear, cracks, or fraying and replace it if necessary.
- Battery Health: Keep your cars battery in good condition by regularly checking its voltage and ensuring proper connections.
- Avoid Overloading: Minimize excessive electrical loads on the system by turning off unnecessary components when not in use.
- Professional Servicing: If you suspect any issues with your alternator, have it inspected and serviced by a qualified mechanic to address problems before they worsen.
By understanding how alternators work and taking appropriate maintenance measures, hybrid car owners can ensure their vehicles continue to run smoothly without any electrical hiccups.
The Evolution of Hybrid Cars and Powertrain Configurations

Hybrid cars have come a long way since their inception, with advancements in technology leading to the development of various powertrain configurations. In the early days, hybrid vehicles primarily used series powertrains.
However, as time progressed, manufacturers started implementing different setups like parallel or series-parallel configurations.
Series Powertrains: The Early Days
In the early stages of hybrid car development, series powertrains were commonly utilized. These systems consisted of an internal combustion engine that powered a generator.
The generator, in turn, supplied electricity to an electric motor which drove the wheels. One notable example is the first-generation Toyota Prius.
Pros:
- Efficient use of fuel due to the engine running at its peak efficiency.
- Regenerative braking helped recharge the battery while slowing down or stopping.
Cons:
- Limited range solely relying on electric power.
- Engine-driven generators resulted in increased fuel consumption during high-demand situations.
Parallel Powertrains: Combining Forces
As hybrid technology advanced, parallel powertrains gained popularity. In this configuration, both the internal combustion engine and electric motor work together to propel the vehicle forward.
The power from both sources can be combined or used independently depending on driving conditions and energy requirements.
Pros:
- Improved overall performance with a combination of electric and combustion engines.
- Greater flexibility in utilizing either source for optimal efficiency based on driving demands.
Cons:
- Limited electric-only range compared to pure electric vehicles.
- Higher complexity and cost due to dual propulsion systems.
Series-Parallel Powertrains: Best of Both Worlds
Modern hybrid cars often employ series-parallel powertrain configurations. These setups offer a balance between efficiency and performance by seamlessly switching between series and parallel modes as needed.
This flexibility allows for optimal utilization of both electric and combustion engines based on driving conditions.
Pros:
- Enhanced fuel efficiency through intelligent management of power sources.
- Extended electric-only range, reducing reliance on the internal combustion engine.
Cons:
- Increased complexity and cost due to the integration of multiple power sources.
- Potential for reduced cargo space due to battery placement requirements.
Hybrid cars have evolved significantly over time, with powertrain configurations adapting to meet changing demands. From early series powertrains to modern series-parallel setups, these vehicles continue to improve their efficiency, performance, and environmental impact.
As technology advances further, we can expect even more innovative powertrain designs in the future.
do hybrid cars have alternators? Debunking the Myth
Contrary to popular belief, hybrid cars do use alternators. However, their operation may differ from that of traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Understanding these differences can help dispel misconceptions about alternator usage in hybrids.
Hybrid Cars and Alternators: Breaking the Stereotype
Hybrid cars are known for their unique powertrain configurations, which combine an internal combustion engine (ICE) with one or more electric motors.
These motors work together to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. While conventional vehicles rely solely on the alternator to generate electricity and charge the battery, hybrid cars have a more sophisticated system.
How Hybrid Cars Generate Electricity
In a hybrid car, electricity is generated through various means, including regenerative braking and the ICE itself. When you apply the brakes in a hybrid vehicle, kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy and stored in the battery for later use. This process helps recharge the battery without relying solely on the alternator.
When driving at high speeds or during acceleration, excess power from the ICE is diverted to charge the battery instead of being wasted as heat like in traditional vehicles. This innovative system allows hybrid cars to maximize energy efficiency while minimizing reliance on an alternator alone.
The Role of Alternators in Hybrid Cars
Although hybrid cars have alternative methods of generating electricity, they still utilize alternators as part of their overall power generation system.
The primary function of an alternator remains consistent across both conventional and hybrid vehicles: it converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy that charges the battery and powers various electrical components.
However, there are some notable differences between how alternators operate in hybrids compared to traditional vehicles:
- Efficiency: Hybrid car alternators are designed to be more efficient than those found in conventional cars since they work alongside other power generation methods.
- Size: Due to reduced reliance on an alternator alone, hybrid car alternators can be smaller and lighter.
- Load Management: Hybrid cars employ advanced load management systems that regulate the electrical demands of various components to optimize overall efficiency. This includes controlling the output of the alternator based on the current power requirements.
Dispelling Misconceptions
The misconception that hybrid cars do not use alternators may stem from their unique powertrain configurations and the utilization of alternative methods for generating electricity.
However, it is important to recognize that while hybrids have additional means of generating power, they still rely on alternators as part of their overall electrical system.
Understanding how hybrid cars generate electricity and the role of alternators in this process helps debunk this myth.
By dispelling misconceptions, we can appreciate the innovative technologies behind hybrid vehicles and their contributions to a more sustainable future.
Exploring Alternatives to Traditional Alternators in Hybrid Cars
Hybrid cars are known for their innovative technologies that maximize efficiency and reduce emissions.
The answer is not as straightforward as it may seem. While traditional alternators are commonly found in conventional vehicles, some hybrid cars utilize alternative technologies that serve similar purposes while offering improved performance and efficiency.
Integrated Starter-Generators (ISGs)
One alternative technology used in hybrid cars is the integrated starter-generator (ISG). Unlike a traditional alternator, an ISG serves a dual purpose by functioning as both a starter motor and a generator.
This means that instead of relying solely on an alternator to charge the battery, an ISG can also generate electricity while the vehicle is in motion. By integrating these functions into one component, hybrid cars equipped with ISGs can achieve greater energy efficiency.
Electric Motor-Generators (MGs)
Another alternative to traditional alternators in hybrid cars is the electric motor generator (MG). Similar to an ISG, an MG performs multiple functions within the vehicles powertrain system.
It acts as both an electric motor for propulsion and a generator for charging the battery during regenerative braking or when excess power is available. By utilizing MGs in hybrid vehicles, manufacturers can optimize energy usage and enhance overall performance.
These alternatives offer several advantages over traditional alternators:
- Improved Efficiency: Integrated starter generators and electric motor generators are designed to be more efficient than conventional alternators. They can recover energy that would otherwise be lost during deceleration or idle periods.
- Enhanced Performance: The integration of starter and generator functions allows for seamless transitions between power modes, resulting in smoother acceleration and improved responsiveness.
- Reduced Emissions: By maximizing energy recovery through regenerative braking and other techniques, hybrid cars with alternative generators can significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions.
Its important to note that while these alternative technologies offer benefits, they also come with their own considerations:
- Cost: Implementing integrated starter generators and electric motor generators can increase the cost of manufacturing hybrid vehicles. However, as technology advances and becomes more widely adopted, costs are expected to decrease.
- Complexity: The integration of multiple functions into a single component adds complexity to the vehicles powertrain system. This may require specialized maintenance and repair procedures.
The Importance of Regenerative Braking in Hybrid Electric Vehicles
Regenerative braking is a crucial feature in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) that allows them to recover energy during deceleration or braking.
This innovative technology captures the energy that would otherwise be wasted as heat and converts it into usable electrical energy.
Lets explore why regenerative braking is so important in HEVs.
Recovering Energy for Battery Charging
One of the key benefits of regenerative braking is its ability to charge the vehicles battery. Traditionally, alternators have been responsible for charging the battery while driving.
However, with regenerative braking, the captured energy can be used to charge the battery instead of relying solely on the alternator. This means that HEVs can harness and store energy that would have otherwise been lost during braking.
Enhancing Fuel Efficiency
By utilizing regenerative braking, HEVs can enhance their overall fuel efficiency. Since they are able to recover energy during deceleration and braking, they reduce their reliance on external charging sources such as gasoline engines or external power outlets.
This means that less fuel needs to be burned or electricity needs to be drawn from the grid to charge the battery. As a result, HEVs can achieve higher miles per gallon (MPG) ratings and reduce their carbon footprint.
Extending Electric Mode Range
Regenerative braking also plays a vital role in extending the electric mode range of hybrid electric vehicles. In many HEVs, there is an electric-only mode where the vehicle operates solely on electric power without using any gasoline.
By capturing and storing more energy through regenerative braking, HEVs can increase their electric mode range. This allows drivers to rely more on electricity rather than gasoline, resulting in lower emissions and reduced fuel consumption.
Smoother Driving Experience
In addition to its environmental benefits, regenerative braking also contributes to a smoother driving experience in hybrid cars. When you step on the brake pedal, regenerative braking kicks in and slows down the vehicle.
This gradual deceleration not only reduces wear and tear on the brake pads but also provides a smoother transition between acceleration and braking. The seamless integration of regenerative braking enhances overall driving comfort for both the driver and passengers.
How Hybrid Cars Generate Electricity Without Alternators
Regenerative Braking and Alternative Methods
Hybrid cars have revolutionized the automotive industry by introducing innovative ways to generate electricity. While traditional cars rely on alternators to produce electrical power, hybrid vehicles take a different approach.
They utilize regenerative braking and other alternative methods to generate electricity.
Regenerative braking is a key feature in hybrid cars that allows them to convert kinetic energy into electrical energy.
When you step on the brake pedal, instead of dissipating the energy as heat like in conventional vehicles, hybrid cars use electric motors to slow down the wheels and simultaneously generate electricity. This electricity is then stored in the battery for later use.
In addition to regenerative braking, hybrid cars employ other alternative methods to generate electricity. These methods include:
- Solar panels: Some hybrid models are equipped with solar panels on their roofs, which capture sunlight and convert it into usable electrical energy. While solar panels alone may not provide enough power to propel the vehicle, they can supplement other charging methods and help extend the range of electric driving.
- Engine-driven generators: Although alternators are not solely responsible for generating electricity in hybrids, they still play a role. In some cases, when additional power is needed or when the battery charge is low, hybrid cars use engine-driven generators to produce electricity and recharge the battery.
- Plug-in charging: Many modern hybrid vehicles offer plug-in charging capabilities. This means that you can connect your car to an external power source (such as a wall outlet) and charge its battery directly from the grid. This method allows for more efficient charging and reduces reliance on internal combustion engines.
Battery Storage and Electrical Systems
Once generated through regenerative braking or other alternative methods, the electricity produced by hybrid cars is stored in high-voltage batteries. These batteries serve as reservoirs of electrical energy that can be used later to power various systems within the vehicle.
Hybrid cars have two main types of batteries: the high-voltage battery and the 12-volt battery. The high-voltage battery is responsible for storing and supplying electricity to power the electric motor, while the 12-volt battery is similar to the ones found in traditional cars and powers auxiliary systems such as lights, radio, and air conditioning.
The electrical energy stored in these batteries is used to drive the electric motor, which works in tandem with the internal combustion engine. This combination allows hybrid cars to optimize fuel efficiency by utilizing both electric power and gasoline.
The Future of Alternator Technology in Hybrid Cars
In conclusion, hybrid cars do indeed have alternators, but their function and role have evolved significantly compared to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
While alternators in conventional cars are primarily responsible for charging the battery and powering electrical systems, hybrid cars utilize a combination of technologies to generate electricity more efficiently.
Through regenerative braking and various alternative methods, hybrids can harness energy that would otherwise be lost during deceleration or idle periods.
As we look ahead to the future, advancements in alternator technology will continue to play a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and performance of hybrid cars.
Manufacturers are exploring innovative solutions such as integrated starter generators and electric superchargers to further optimize energy generation. These developments not only contribute to reducing fuel consumption but also pave the way for cleaner transportation options.
So if youre considering purchasing a hybrid car, rest assured that they do have alternators, albeit with improved functionality.
By harnessing wasted energy and embracing cutting-edge technologies, hybrid vehicles offer an environmentally friendly solution without compromising on power or convenience. Take the leap into the world of hybrids and join the movement towards a greener future!
FAQs
Can I rely solely on the electric motor in a hybrid car?
While it is possible to drive a hybrid car solely on electric power under certain conditions, most hybrids still require some assistance from the internal combustion engine. The electric motor provides additional torque during acceleration and assists with fuel efficiency by allowing the engine to operate at its optimal range.
Do hybrid cars require special maintenance?
Hybrid cars generally do not require any additional maintenance compared to traditional vehicles. However, it is essential to follow regular service intervals recommended by the manufacturer for routine check-ups of both electrical and mechanical components.
Are hybrid cars more expensive than conventional vehicles?
Initially, hybrid cars may come with a higher price tag due to their advanced technology. However, over time, you can potentially save money on fuel costs, tax incentives, and reduced maintenance expenses. Its worth considering the long-term benefits and potential savings when making a purchasing decision.
Can I charge a hybrid car at home?
Unlike fully electric vehicles, most hybrid cars do not require external charging stations as they rely on regenerative braking and the internal combustion engine to recharge their batteries. However, some plug-in hybrid models offer the option to charge from an external power source for an extended electric-only driving range.
Are hybrid cars suitable for long-distance travel?
Hybrid cars are well-suited for both short commutes and long-distance travel. The combination of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor provides ample power and range, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of fuel efficiency without compromising on comfort or convenience during longer journeys.