How long do electric cars last

EV Lifespan: Do They Last as Long as Gasoline Cars?
Just as gasoline and diesel engines were once new technology and poo-pooed by the horse-driven public, modern battery electric vehicles (EV) are facing the same criticisms. Will electric vehicles be on the road as long as gasoline cars and diesel vehicles? Absolutely, and automakers are already delivering.
Myth Busted: Neither EVs nor Gasoline Cars Are Infallible
Since the first automobile went from production to daily driver to a cube at the junkyard, car and truck lifespan has been increasing. Notwithstanding a few outliers, such as Irv Gordons 3.2-million-mile 1966 Volvo P1800S and Matt Farahs million-mile 1996 Lexus LS400, the increasing life of the typical car is encouraging. In 1977, the average American car was just 5.5 years old. By 1995, it was 8.4 years, and in 2020, the average reached 11.9 years.
That says a lot about todays typical driver expectations and the technical advances implemented to meet them: People want cars that last. EV or gasoline-powered, they expect any car they buy today to be safe, efficient, and reliable years down the road.
Still, where and how any vehicle is driven and maintained has a significant impact on lifespan, regardless of how well an auto might be built. Harsh driving, overloading, corrosion, and neglect will destroy any vehicle before its prime, but well-maintained vehicles are no longer considered worn-out until theyve reached at least 150,000 miles.
No vehicle is infallible but there are some things that tend to give EVs a better shot at a longer lifespan.
EV Key Component Life Expectancy
When youre trying to decide between buying an electric vehicle or a conventional vehicle, there are several shared components to take out of the lifespan comparison. Both types include the following similarities:
- Modern vehicle frame and body construction last the life of the vehicle, depending on environmental factors.
- Electrical systems, such as the radio, navigation system, headlights, taillights, and power windows, generally last upwards of 10 years.
- Steering and suspension components typically last 6 to 10 years.
- Tires generally last 4 or 5 years, depending on driving habits and alignment maintenance.
- Wipers and cabin filters are typically replaced every 6 to 12 months, depending on environmental factors.
- The 12-V battery is also the same, lasting typically 5 to 7 years in typical driving.
- Brake hydraulics and calipers are the same, typically requiring service every other year.
On the other hand, major differences do exist between conventional vehicles and electric vehicles. While modern conventional powertrains, with proper maintenance, are proven to last, electric vehicle batteries and motors arent often given a fair look, mostly because of the expense of critical components like batteries.
Even so, major electric vehicle components are at least as good as their gasoline-chugging counterparts.
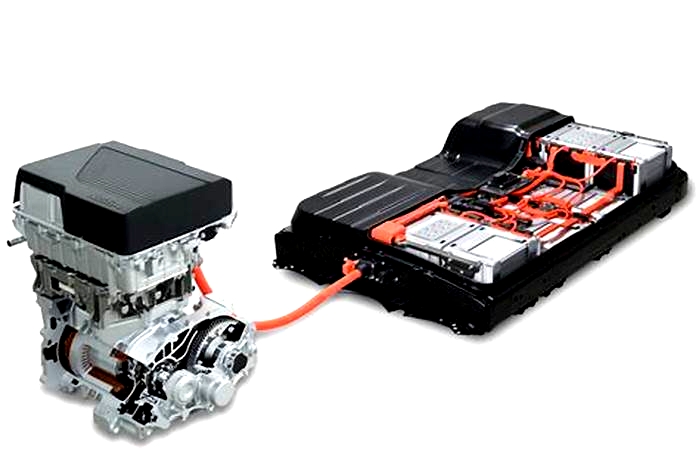
Motor
monkeybusinessimages/iStock/Getty Images Plus
Electric motors typically have a single moving part, in comparison to several hundred parts in an engine. Electric motor maintenance is limited to coolant changes every 100,000 miles. Engines, in addition to coolant, require regular oil changes, air filters, and likely spark plugs in that time. Both motors and engines are proven to last upwards of 20 years.
Transmission
da-kuk/Getty images
Since electric vehicles usually arent equipped with a transmission, just a single gear reduction, theyre the clear winner in the transmission lifespan comparison. For modern conventional vehicles, manual and automatic transmissions typically last upwards of 15 years, requiring fluid services at least every 100,000 miles.
Battery
Tesla
Lithium-ion battery packs are expensive, but they last a long time. So far, the typical EV battery has been proven to last about 200,000 miles, nearly 20 years. Tesla is rumored to be developing an EV battery that will last 1,000,000 miles, much longer than the average vehicle, currently 11.9 years. Major EV makers report few battery replacements in the last decade.
Brakes
Brake services offer an interesting comparison. Because electric vehicles use regenerative braking to slow the vehicle, the hydraulic brake system isnt used as much. While conventional vehicle brakes last 25,000 to 65,000 miles, depending on vehicle type and driver habits, hybrid and EV pads and rotors are known to last much longer. Some hybrid and EV owners report their brakes lasting over 100,000 miles.
EV Maintenance Matters!
Electric vehicles simpler powertrains require less service, which actually makes required services more critical. How you drive, charge, and maintain your electric vehicle will play a big part in how long it lasts, just like it does with a gasoline-powered vehicle. There are two key areas to pay attention to.
Cooling System Checks
Cooling system maintenance is important. A combination of active and passive heating and cooling keep the battery pack around 70 F for best lifespan. Pay close attention to cooling system maintenance, such as coolant or air filter replacement.
Battery Charging Practices
Charging practices are critical. While the battery management system (BMS) manages charge rates to protect the battery, you can do your part by charging mainly on Level 2 chargers. You can use Level 3 charging stations on trips, but regular consistent usage of these high-power chargers will impact battery life.
EV Life Expectancy Is at Least Equal to Gas Cars
Given technological advances in both conventional and electric vehicles in the last decade, neither seems to have longevity issues. With responsible driving and maintenance habits, both should last at least a decade, if not much longer.
Government and automaker confidence seems to reflect the desire, if not the reality, of EV longevity. To help encourage confidence in EVs, federal rules now require automakers to cover major components, like the battery and electric motor, for eight years or 100,000 miles, while California extends that to 10 years or 150,000 miles. Some EV automakers even offer a lifetime guarantee, something practically unheard of in conventional vehicle warranties.
If youre shopping for a new vehicle, its good to know you can choose any car that suits you best. Eventually, as pricing and availability become more competitive, its likely that not choosing an electric vehicle will seem like a risky bet.
How-To Geek
The lithium-ion battery packs in an electric vehicle (EV) may be akin to the one in your cell phone, but do they degrade as quickly? We take a look at how long an electric car's battery really lasts.
Related: How Does an Electric Vehicle Work?
How Do Electric Car Batteries Work?
EV batteries are actually battery packs full of groups of individual lithium-ion cells, each of which can store a certain amount of power. As you drive around and use the car's electrical systems, that stored energy is discharged until the battery needs to be topped up again.
The life of an EV battery is commonly measured in charge cycles---that is, the number of times the battery is fully charged and discharged. As with other devices powered by lithium-ion cells, the amount of charge the battery can hold will decrease as the battery pack degrades over time. The battery in your smartphone, for example, might start to degrade after just a couple of years of use.
Thankfully EV batteries are built sturdier than that and the technology is constantly improving. Most car manufacturers have a five to eight-year warranty on their EV batteries. Tesla offers an eight-year warranty with unlimited mileage on the Model S, and Nissan backs their Leaf for eight years or 100,000 miles, whichever comes first.
An EV's battery capacity is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). According to MyEV, the higher the rating, the better:
"An electric car's battery capacity is expressed in terms of kilowatt-hours, which is abbreviated as kWh. More is better here. Choosing an EV with a higher kWh rating is like buying a car that comes with a larger gas tank in that you'll be able to drive for more miles before needing a 'fill up.'"
Pretty much all EVs are also built to keep their batteries from charging all the way to 100% or completely losing their charge. That helps extend the battery's overall lifespan. Factors like extreme temperatures, driving at higher sustained speeds, and how much you use the car's peripheral electronics will also affect how much you get out of each charge.
Lithium-ion batteries are lighter than the lead-acid batteries used in gas-powered cars, and are more energy-dense than rechargeable nickel-hydride batteries, making them the logical choice for powering an EV. Changes in the metal and chemical composition of these batteries in recent years mean we could see even higher energy capacity and shorter recharge times in future generations of EVs.
How Many Years Does the Battery Last?
Your individual driving habits will affect the lifespan of an EV's battery, but most manufacturers cover their battery packs for at least eight years, and anywhere from 10,000 to 100,000 miles. Tesla and Hyundai cover their EV batteries for life. Read the fine print here, though---some manufacturers will only replace the battery in the event of complete failure, which is exceedingly rare.
So how long can you drive an EV before the battery starts to lose charge capacity? It varies by manufacturer and use conditions, but it's usually a very gradual process. EV advocacy group Plug In America collects data from EV drivers on changes in charge capacity over time and found that Tesla Model S vehicles usually only lose around 5% of their total charge capacity after the first 50,000 miles of driving.
The bottom line? MyEV says that, when properly cared for, an EV's battery should get you well past the 100,000-mile mark before its capacity is limited. Some estimates range as high as 200,000 miles. When driven around 12,000 miles per year, that's around 17 years before the battery needs to be replaced. That's somewhat less than the average mileage of 15,000 per year logged by drivers in North America but still promising.
Related: Level 1, Level 2, or Level 3? EV Chargers Explained
Some things will shorten your battery's lifespan if done too often. Using fast charging stations all the time, for example, can burn out the battery faster because it's receiving a lot of electricity very quickly. Extreme cold slows down the chemical reactions that take place in a lithium-ion battery and can affect capacity. Extreme heat can also reduce a battery's charge capacity, but most EVs are equipped with a cooled battery back to mitigate that.
Conversely, steps like only charging the battery when necessary and staying between 20-80% capacity will help extend the life of an EV's battery pack, according to EVBox.
What Happens to Old EV Batteries?
EV manufacturers are working on ways to both repurpose and recycle old batteries once they've died or lost the capacity to power a vehicle. Completely dead batteries are usually recycled by being separated into their component metals, which are then used to rebuild new batteries. Only about half of a battery's components can be recycled as of this writing, but new methods are being developed to glean more valuable metals from an EV's battery at the end of its life.
Batteries with some capacity left can be repurposed to provide power in other ways. As backup batteries for homes, for example, or used to store energy from solar panels.
How Long Do Electric Cars (& Their Batteries) Last?
Electric cars will define the future of the automotive industry. Practically every automaker is investing millions of dollars into electric car technology, and this is occurring for every type of vehicle from small economy cars to pickup trucks to supercars and hypercars.
On the performance side of things, electric cars are actually often more impressive than their internal combustion counterparts. The instant torque provided by an electric motor makes for fast acceleration. On the other hand, electric cars have some work to do when it comes to charging times and batter range.
Overall, though, electric cars are a viable option for most drivers, and this leads to a lot of people asking questions about how long EVs last and what the maintenance on an electric car is like. Well, lets take a closer look at these questions.
Whats the Longevity of an EV and Its Batteries

The car itself should last for decades, electric cars are built on similar chassis designs to other cars, so the body, wheels, suspension, and everything not powertrain related will last just as long as any other car.
When it comes to the battery and powertrain of electric vehicles, its mostly good news. Electric motors have far fewer moving parts than an internal combustion engine. The single-speed transmission found in most electric cars is a lot simpler than the transmission found in internal combustion engine cars, too. These simpler components with fewer moving parts should last a really long time.
As for the batteries in electric cars, theyre lithium-ion batteries. This means they provide a greater energy density than typical lead-acid batteries. They hold a charge for a long time even when not in use, and they can be charged time and time again without too much degradation.
Every electric car in sold in the U.S. comes with a battery warranty of eight years or 100,000 miles. Many come with a 10-year or 100,000-mile battery warranty. A few companies, like Hyundai, provide a lifetime battery warranty.
Coverage for the warranty is usually dependant on the level of charge the battery can hold. If it falls below 60 or 70 percent of its capacity, then you can get it replaced and the warranty will cover it, according to Carfax. That is just for most automakers, though. Some require the battery to be unable to hold a charge at all.
As for how long a battery in an electric car actually lasts, well, it really depends on a variety of factors, including temperature and the type of charger you use, according to Carfax.
Lithium-ion batteries struggle with heat, so if you live in a very hot environment, youll often notice your battery losing its ability to hold a charge sooner than if you live in a place with moderate temperatures.
Also, Carfax notes if you quick-charge your car all of the time, you will hurt the batterys longevity. Slower charging is typically better for battery life. This can also be connected to heat because fast-chargers produce a lot of it when theyre operating.
However, all factors aside, batteries in electric cars should last around 200,000 miles, according to MY EV. Thats about the same amount of miles you can get on many cars with internal combustion engines if you take good care of them. In terms of years, thats usually over a decade of driving, depending on how much you drive. The cost of ownership of an electric car will likely be far less all things considered.
This will only get better in the future. Elon Musk, the founder of Tesla, has discussed million-mile batteries in the future. These batteries could be recharged time and time again until the car has driven 1 million miles. That, however, is a little bit down the road.
Whats the Maintenance on an EV Like

In general, electric cars will have far less maintenance than a car with an internal combustion engine. The far fewer parts mean the powertrain will not need much regular maintenance. This means no oil changes, coolant changes, or air filter changes, and all of those other things youre used to doing every few thousand miles.
Of course, there is still some maintenance. Youll need to do tires and brakes on a regular schedule. Also, your suspension will need occasional maintenance. Lights and electrical systems will also need service from time to time, but these intervals are generally few and far between.
This can help you save a good amount of money a year in maintenance costs and thousands over the course of the time you own the car.
With that said, whether or not youll actually save money driving an EV is a hotly debated topic. In a AAA survey, it was determined that an ICE car is actually cheaper when you factor in depreciation and insurance into the equation by $590. This is with tax credits factored in as well.
| AAA Survey Findings | EV | ICE |
| Fuel: | 546 | 1,255 |
| Maintenance/Repair/Tires: | 949 | 1,279 |
| Insurance: | 1,214 | 1,328 |
| License/Registration/Taxes: | -579 | 466 |
| Depreciation: | 4,806 | 2,240 |
| Finance: | 768 | 546 |
| Total Per Year | 7,704 | 7,114 |
However, InsideEVs notes that the survey left out Tesla cars and only included legacy automakers, so there were not really that many models included. Its also worth noting that hybrids of all kinds were excluded, and only a few ICE cars were used for comparison.
That means theres some question as to the validity of the survey. Also, if you take out the depreciation factor and look just at what youll actually pay while you own the car, youll see that the situation is dramatically different. Instead of the ICE car being $590 less expensive, its actually $733 more expensive. This means if you take out depreciation as a factor, electric cars are less expensive to own and maintain.
AAA isnt the only one doing this kind of survey. Recently, Consumer Reports did an analysis of the total cost of owning an electric car vs an ICE car. The analysis showed that battery-electric cars and plug-in hybrid cars are much cheaper to own and operate. Battery electrics cost around $0.012 per mile and PHEVs cost $0.028 per mile. ICE cars on the other hand cost around $0.031 per mile to operate.
The repair cost data between 100,000 and 200,000 miles happens to show more of the same. Battery electric vehicles cost $0.043 per mile, PHEVs cost $0.033 per mile, and ICE vehicles cost $0.079 per mile.
In terms of fuel savings, a battery-electric vehicle will save $790 over the course of 15,000 miles compared to an ICE car. If you compare an electric SUV to an ICE SUV, youll get even better savings of $1,020.
The methods used for the study were a little more sound than AAA used for its survey, but its still not perfect. The sample size for some metrics like the repair cost analysis was on the smaller side. Still, the data shows that massive savings of thousands of dollars over the course of the cars lifetime. in some cases its up to $23,000 if you compare battery-electric cars to ICE cars with similar acceleration.
In the end, Consumer Reports indicated that buying a used EV could be one of the best ways to get a good, affordable-to-own vehicle. It showed that savings from buying a five-to-seven-year-old EV instead of an ICE car should be two to three times higher than buying a new EV. This means that the reduced maintenance and lower costs of operating, in general, will save you money, and if you buy a used EV, it will save you tons of money.
What Happens When an EV Gets Older?

When an EV gets older, you will see the battery deplete some. This is natural. As a battery gets charged up and discharged, again and again, the battery will lose the ability to hold the same amount of power.
That depletion is somewhere around five to 10 percent for every 75,000 kilometers driven (about 47,000 miles), according to Battery University. You can check out the graph below to see just how a battery degrades over time.

The degradation of the battery is directly tied to the number of battery cycles you put the car through or how many times you charge the car.
As was mentioned above, this depletion can be increased by using fast chargers often. If you want to make the most of your electric cars battery, then you should really use a Level 2 charger or lower.
The battery and electric motor should be good well after the car is 10 years old and it could continue to be a great vehicle all the way up to 15 or even 20 years, depending on how well its taken care of and how far youre driving.
Again, a variety of factors matter, including temperature. In excessively cold temperatures, battery life should not be impacted, though the amount of power you can get in each charge will. However, if a battery is in extremely hot conditions, then it could see a reduction in overall life.
Its important to note that the rest of the car will age like any other car. This means that suspension will wear out, excessive moisture and the use of salt on the road (Im looking at you Midwestern America) will cause rust, and many other things that happen to cars as they age will.
In general, though, you can rest assured that an older EV will function very much as it should unless it has been thoroughly neglected or was in an accident of some kind.