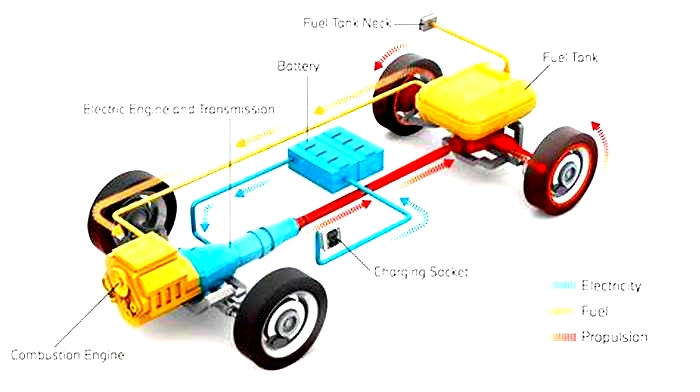
The Future of Electric Vehicle Racing Faster More Sustainable Competition

Green Transportation for a Greener Future: Modes and Benefits
In an era characterized by escalating environmental concerns and climate change, the need for sustainable and eco-friendly transportation has never been more urgent. Green Transportation for a Greener Future: Modes and Benefits delves into the various modes of environmentally-conscious transportation and explores the extensive benefits they offer. By transitioning from conventional transportation options to greener alternatives, we can significantly reduce carbon emissions, alleviate traffic congestion, and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Electric vehicles have gained remarkable popularity as a viable alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. EVs run entirely on electricity, producing zero tailpipe emissions and significantly reducing air pollution. As advancements in battery technology continue, EVs are becoming more affordable and capable of longer distances, making them a promising choice for eco-conscious commuters.
2. Public Transportation:
Public transportation systems, including buses, trains, and subways, are essential components of sustainable mobility. By encouraging the use of shared transport, we can minimize the number of individual vehicles on the road, thus reducing congestion and emissions. Well-planned public transit networks provide an efficient, cost-effective, and eco-friendly means of commuting.
3. Cycling and Walking:
Active modes of transportation like cycling and walking are not only beneficial for personal health but also for the environment. They produce zero emissions and require minimal infrastructure, contributing to reduced congestion and improved air quality. Cities with well-designed bike lanes and pedestrian pathways promote a healthier lifestyle while decreasing reliance on fossil fuel-based transportation.
4. Carpooling and Ride-Sharing:
Carpooling and ride-sharing initiatives encourage the sharing of rides among multiple passengers traveling in the same direction. By reducing the number of vehicles on the road, these practices decrease greenhouse gas emissions, ease traffic congestion, and save participants money on fuel and maintenance costs.
Benefits of Green Transportation:
1. Environmental Impact:
The adoption of green transportation modes significantly lowers carbon emissions and reduces air pollution. Electric vehicles and other sustainable options release fewer pollutants, helping mitigate the detrimental effects of climate change and improving air quality in urban areas.
2. Energy Efficiency:
Green transportation modes are generally more energy-efficient compared to their conventional counterparts. Electric vehicles, for instance, convert a higher percentage of stored energy into actual propulsion, leading to reduced energy consumption and fossil fuel dependency.
3. Cost Savings:
While the upfront costs of some green transportation options might be higher, the long-term savings in terms of fuel and maintenance expenses often outweigh the initial investment. Public transportation, cycling, and walking are also budget-friendly alternatives.
4. Reduced Congestion:
By encouraging shared modes of transportation, such as carpooling and public transit, green transportation systems help alleviate traffic congestion in urban areas. This leads to shorter commute times and less stress for travelers.
5. Health Benefits:
Active transportation modes like cycling and walking promote physical activity, leading to improved cardiovascular health and overall well-being. Additionally, reduced air pollution from green transportation positively impacts public health by decreasing respiratory problems and related diseases.
we can conclude this, Green Transportation for a Greener Future: Modes and Benefits underscores the pivotal role of sustainable transportation in shaping a more environmentally-conscious and prosperous future. By embracing electric vehicles, public transportation, active modes like cycling and walking, and ride-sharing initiatives, we can collectively contribute to reduced carbon emissions, improved air quality, and enhanced quality of life for ourselves and future generations. Through informed choices and concerted efforts, we can drive the transformation toward a greener transportation landscape.
FAQs
1. What exactly is green transportation?
Green transportation refers to the use of environmentally-friendly modes of travel that produce minimal or no negative impact on the environment. It includes options like electric vehicles, public transportation, cycling, walking, and carpooling, all of which aim to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability.
2. How do electric vehicles (EVs) contribute to a greener future?
Electric vehicles (EVs) operate solely on electricity, emitting zero tailpipe emissions. This means they dont produce harmful pollutants that contribute to air pollution and climate change. By adopting EVs, we can significantly reduce our carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels.
3. Why is public transportation considered green?
Public transportation, including buses, trains, and subways, is considered green because it enables multiple passengers to share a single vehicle, reducing the overall number of cars on the road. This leads to decreased traffic congestion, lower emissions, and improved air quality in urban areas.
4. How can cycling and walking be effective modes of green transportation?
Cycling and walking are green transportation options that produce zero emissions and have minimal impact on the environment. These active modes of transportation not only contribute to reduced pollution but also promote personal health and well-being.
5. Are there financial benefits to using green transportation?
Yes, there are financial benefits to using green transportation. While some eco-friendly options might have higher upfront costs, they often lead to long-term savings due to reduced fuel and maintenance expenses. Public transportation, cycling, and walking are also cost-effective alternatives compared to owning and operating a private vehicle.
Like this:
Like Loading...
The Future of Electric Vehicles in India: Opportunities and Challenges
As one of the world's largest automobile markets, India's country-wide electrification will be a turning point for the entire world and the country itself. Driven by theIndian government's push towards sustainable mobility, growing consumer demand for new technologies, and the emergence of private players with an interest in EV technology, the future of electric vehicles in India looks promising.
However, the country continues to grapple with several challenges in its pursuit of full EV adoption, namely with the low number of charging stations and high upfront costs of EVs.
In this article, we focus on the following three questions:
- What is the state of the Indian EV ecosystem?
- What challenges and opportunities lie ahead?
- What can India learn from other countries?
India's EV Market Is on a Rapid Growth Trajectory
India is one of the world's largest markets for two- and three-wheeled vehicles, ranking among the global top five for private cars and commercial vehicles.
According toJMK Research, a staggering 455,733 EV units were sold in FY2022. India'sMinistry of Road Transport and Highwaysalso claimed that 1,334,385 electric vehicles in India were on the road as of July 2022.
These numbers are sure to increase, with central and state governments, as well as private sector players, actively pushing for greater electrification on Indian roads.
India Sets Ambitious Targets
According to Union Minister Nitin Gadkari, the Indian government intends to achieve the following EV mix in India by 2030:
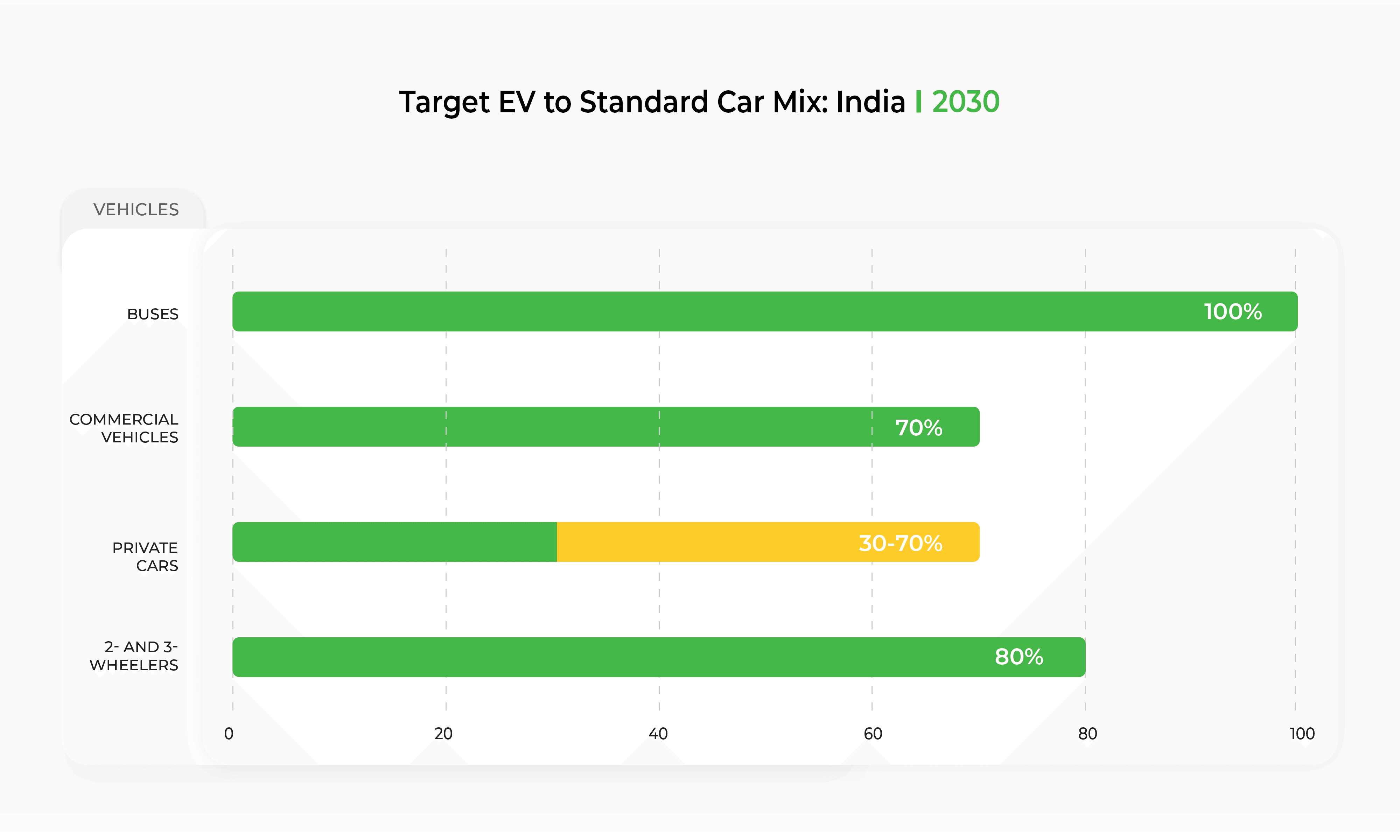
To reach these ambitious targets, the Indian government has created policies and programs likethe National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP), a broad plan to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles in India. The aim is to reduce India's dependence on crude oil.
The Indian government has also formulated the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme. This plan should facilitate greater adoption rates in the coming years. The Finance Minister of India has alsoannounced a reduction in customs duty and taxesfor the 2023 budget. This will help boost the domestic production of lithium-ion batteries that power electric vehicles.
Many state governments like Assam, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, and Gujarat have alsocreated attractive policies and programsto incentivize EV manufacturing in their respective territories.
As a result of these strategies, private players have begun entering the EV market, setting the stage for the further adoption of electric vehicles in India. India's success will also have a significant, positive impact on the rest of the world.
India's EV Adoption Will Be a Global Win
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA),global EV sales in 2021 doubled from the previous yearto 16.5 million EV units sold worldwide. India also announced that EVs will represent at least 30% of all road traffic by 2023. Though a modest target, a 30% adoption rate will have global ripple effects, both environmentally and economically.
For starters, India is the world'sthird-largest oil importer, but the transition to EVs will significantly reduce its oil dependency, disrupting global oil markets. If India can meet its ambitious adoption targets, the country will create a model that other emerging economies can replicate. This, in turn, will have further impacts on oil markets as the dependency on this fossil fuel decreases.
Additionally, withIndia's population of 1.4 billionand its rapidly growing economy, the country is certain to be an influential player in the global EV market today. The full adoption of electric vehicles in India will represent a major step in the right direction toward sustainable development in worldwide mobility.

Subscribe to our Newsletter
Environmental Opportunities for India
The shift towards electric vehicles in India will have a significant impact on the environment. Currently, the transportation sector in India is a major contributor to pollution. Take the capital, New Delhi, for example, wheretwo- and three-wheelers contribute 50% to the surface PM 2.5levels.
India's transportation sector also accounts forabout one-fifth of the country's total energy use. In light of these numbers, EVs can have a huge impact on India's environment in the following areas.
1. Reducing Air Pollution
Within India alone, vehicular traffic contributes to 27% of total air pollution andclaims 1.2 million deathsannually. EV adoption in India will therefore significantly reduce the negative global environmental impacts originating from Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles.
2. Reducing Noise Pollution
Noise pollution is also a major challenge in India due to the rapid urbanization increasing the need for vehicles. According to the2022 UNEP report, five Indian cities feature in the world's noisiest cities. Though vehicles are not the only source mentioned in the report, EVs are likely to bring down the noise levels because they don't have the mechanical valves, gears, or fans common to ICE vehicles.
3. Improving Operational Efficiency
From a fuel efficiency standpoint, petrol or diesel cars convert only17 to 21% of stored energy while EVs can convert 60% of electrical energyfrom the grid. Clearly, this shift to electric vehicles in India can improve the efficiency of fuel production and optimization. It will bring down the operational costs for end-users, thereby increasing demand for EVs.
Besides the above environmental impacts, the adoption of EVs in India will also present many economic opportunities for the country.
Economic Opportunities for India
In addition to representing significant progress towards a cleaner and greener future, locally, the full electrification of India will benefit businesses, investors, and consumers alike. Below, we highlight several of the most compelling opportunities.
1. Fleet Operators
Fleet operators like Amazon, DoorDash, and BigBasket can reduce their operating costs by switching to EVs. According toWeforum.org, the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) for a two-wheeler in New Delhi is Rs 2/km when it's run on petrol. This cost comes down to Rs 0.52/km when switched to EVs. Undoubtedly, the operating costs go down by more than half for fleet operators. Maintenance costs will go down as well.
However, shifting to EVs is happening at a much slower pace when compared to Brazil or the US. Electric vehicles in India are still unfavored because of the high upfront costs, unestablished reseller value, and lack of trust in the new technology.
To address these concerns, the government is providing tax incentives to reduce upfront costs. Meanwhile, first mover companies are providingrobust and reliable charging solutionsthat will boost confidence in this new technology.
2. OEMs
The EV industry provides enormous opportunities for OEMs to build cost-competitive auto products for India and the rest of the world. Research shows that OEMs canproduce a 5.7% higher value addition to every EV by 2030. As a result, the Indian government is pushing for indigenization of the supply chain under the Atma Nirbhar plan to support OEMs to develop the EV ecosystem.
Furthermore, efforts from companies in India are underway to help OEMs build acharging app using SDK development tools, and provide access to features like navigation, vehicle diagnostics, and keyless control. All these measures help OEMs offer on-the-go charging for their drivers and accelerate the shift to EVs.
3. The Real Estate Sector
EVs create multiple opportunities for real estate investors, realtors, and property developers, as this industry requires theconstruction of EV manufacturing units, industrial areas, and charging stations. Another key aspect is the development of retail infrastructure around EV charging stations, as it takes an average of 15 to 20 minutes to charge an EV.
Areport by Colliersshows that the EV industry will require 1,300 acres to set up 110 GWh battery manufacturing capacity by 2030. The country will also need 13.5 million square feet for charging stations by 2025. These numbers reflect the ample opportunities available for every player in the real estate space.
4. Consumers
India's young and dynamic population is looking forward to embracing new technologies as the country is experiencing agrowing trend in upward mobility. As individuals become more affluent, their socioeconomic status continues to improve, and they are better positioned to purchase EVs.
To meet the growing demand, the government and other innovative players in India's EV space are spearheading efforts to add more charging points to EV charging networks. This includes offering software solutions that make daily charging accessible.
Multiple players are alsopartnering with businesses and government agenciesto build innovative solutions that positively impact the EV industry, leveraging India's qualified talent pool. According toNitin Gadkari, the Union Minister of Road Transport and Highways, the EV industry is likely to create five crore new jobs, and India's young talent pool is well-poised to ride this job growth.
Despite these many opportunities, the country still has to address significant challenges before reaching full adoption of electric vehicles.

The Challenges for India
Realizing India's EV potential is not without its challenges. The journey towards widespread EV adoption in India is slow and plagued with hurdles to overcome. In the following sections, we examine the key challenges hindering EV adoption in India. We also explore possible solutions that can help the country overcome these obstacles to enable a faster, more efficient country-wide adoption of EVs.
1. Lack of Clean Energy
Much of India'selectricity is generated from burning coal. That said, relying on coal to generate power for all the EVs would defeat the purpose of reducing carbon emissions through EV adoption. That's why India is exploring other energy generation sources, like solar, wind, and nuclear energy, as mentioned in Nitin Gadkari's speech in the7th edition of the ETAuto EV Conclave. The government is also actively pursuing research and development in the areas of biofuel to power EV manufacturing units.
These measures from the Indian government provide trust and opportunities for private players to leverage innovation and technology to build EVs faster and at a lower cost. In turn, this will bring down upfront costs for end-users, thereby leading to greater adoption of electric vehicles in India.
2. Underdeveloped Charging Infrastructure
Infrastructural issues stand against India's quest for full EV adoption. EVs require different charging and maintenance infrastructure than traditional ICE vehicles because of the differences in engine and other working parts. But India's current charging infrastructure may not be enough to handle the increased demand for EVs.
At the time of writing this piece, India has934 charging stations, most of which are located in urban areas. In comparison,China had 1.8 million electric charging stationsas of 2022. Building bigger batteries and fast-charging stations will mean investing in high-speed, commercial-grade chargers. This, however, requiressignificant capital investment.
The government is working with private players to boost the presence of charging stations. TheMinistry of Poweris providing a slew of financial and non-financial incentives to build EV charging stations. For example, the ministry is adopting a revenue-sharing model for land use and setting affordable charging rates for both operators and users.
In addition, private entities in the sector are working with municipal, state, and central entities to helpinstall EV stations and charging points. They are also collaborating with operators to create a Charger Management System (CMS) to monitor the operations of these stations and streamlining the entire charging process.
3. Suboptimal Battery Technology
An EV's driving range is limited, making it difficult for drivers to travel long distances without recharging. Besides limited charging stations, battery capacity, aerodynamic drag, and vehicle weight also compound the problem. This is because current batteries are small, and have low voltage capacities, so they aren't enough to increase EV propulsion and travel longer distances.
To address this problem, private players must innovate to create batteries made of lightweight materials, with higher energy density, and that use renewable sources for charging. The government is providing the necessary impetus in the form oftax credits.
The national government is also promoting the manufacturing of batteries in India with theNational Mission for Transformative Mobility and Battery Storage, 2019. It is also providing companies with the technical know-how and business environment to improve the battery technology for EVs.
4. Persistent Resistance to Change
Indian consumers are still resisting the adoption of EVs, despite their long-term economical and environmental benefits. This stems from a lack of awareness of EVs and a general reluctance to embrace new technologies, especially in rural areas.
But players in the Indian market must come together to address consumers' concerns. They should also build a supportive ecosystem to promote the widespread adoption of EVs in India. This can be done through the development of more affordable EVs, the expansion of charging infrastructure, and the creation of awareness and education programs to educate consumers about the benefits of switching to EVs.
What Can India Learn from Other Countries' Success?
Power, infrastructure, and financing all are primary antagonists in India's EV adoption story. But the country can take cues from others already making inroads towards full EV adoption. The countries leading global EV adoption paint an interesting picture.
The top countries in the graph above are all wealthy countries in northern Europe. Combined, they don't even represent 3% of India's population. This may lead us to believe that their success will be impossible to replicate in a much more diverse and densely-populated country, like India.
However, Chinacomes in second and turns that argument on its head. Let's delve into what different regions have done for EV adoption and what India can learn from these efforts.
The EU, EFTA, & UK
In 2021,electric car registrationsin the EU-27 region was 1,729,000, up from 1,061,000 in 2020, representing a 17.8% increase. All EU countries, including Norway, which has the highest number of registrations in a year, offered financial incentives like tax reductions and exemptions.
India is also offering tax incentives along the same lines. And with favorable government policies and the presence of first-mover companies, the country will be able toimprove the adoption of EVs in the next three to five years.
China
According to the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM),China sold 6.89 million EVs in 2022alone. It also boasts the largest electric car fleet in the world: 4.6 million + electric cars on roads in China. Thissuccess storyis attributed to generous government support as well as intense domestic competition, both of which fueled innovation and reduced car prices.
In comparison, India is also offering support, but the domestic market is not robust and competitive yet. But that is expected to change in the coming years as the impact of the current policies becomes more widespread. In the meantime, the government must continue to encourage innovation and investments.
The USA
EV car sales in the US represent 5.8% of all vehicles sold, up from 3.2% a year ago. However, the overall sales fell by 8% in 2022 when compared to 2021. Experts believe that stricter requirements for claiming federal incentives, high car prices, and concerns about raw materials for batteries were the cause of the decline. That said, the EV car industry is still huge in the US, and it grew due to government investments and policies. Innovation by leading players like GM and Tesla also added to the appeal.
In comparison, the Indian government is significantly pushing towards greater adoption of EVs, with incentives and investments. However, it must enhance the pace of innovation and technical expertise. To do that, the government should create more educational centers of excellence. It must also stop federal funding in a phased manner after considering the macroeconomic factors.
With the right mix of policies, awareness, investments, infrastructure, and technology, India will certainly take key lessons from these countries to drive full EV adoption.
Smart Digital Solutions Will Be A Key Driver for India's EV Ecosystem
The future of electric vehicles in India holds great promise and is poised for significant growth in the coming years. With supportive government policies, increasing consumer awareness, and advancements in EV technology, the country is well-positioned to embrace this shift toward sustainable transportation.
The increasing demand for EVs is also leading to an expansion of charging infrastructure and the development of locally produced battery technologies. The automotive industry in India is also poised to play a major role in the global shift towards EVs, with the country having the potential to become a leader in this space.
Private companies play a critical role in offering smart digital solutions that will contribute to infrastructure development while acting as a bridge between government agencies and end-users.Initiatives from these companies will help fleet operators make the shift to EVs and OEMs to provide seamless driving experiences to their customers.
Collaboration with local governments will also help expedite the construction of charging stations, along with creating greater awareness among Indian customers. This will contribute to the rapid growth of the EV industry.
It is therefore up to both the public and private sectors to continue working together to make India's ambitious goals a reality. The right combination of innovation and investment has the potential to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles in India, transforming the country's transportation landscape and contributing to a cleaner, greener future.
For more information about the future of electric vehicles in India, please see theFAQandResourcessections below.
FAQ
What challenges is India facing on the road to electric mobility?
India's concerns along the road to electric mobility relate to a lack of infrastructure, energy, and domestic innovation and production. But innovative players are offering solutions and helping pave the way to mass adoption.What will contribute to Indias EV goals?
The Indian government has set ambitious targets for EV adoption in India by 2030. The important contributing factor in meeting these targets is the infrastructure needed to charge EVs in India. EV drivers, however, could install simple and cost-effective solutions. This will help them build on this adoption and accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles in India.Is the future of electric vehicles in India cost-effective?
Many people only see an EVs higher upfront cost, so they assume an electric future is expensive. That said, EVs offer significant savings in maintenance and power over their lifetime. Some companies even enable EV drivers to charge at home while generating passive income from letting others use their device.What are the benefits of electric vehicles?
EVs help reduce carbon emissions. They're also significantly cheaper to run and maintain than traditional petrol-engine vehicles. EVs are even quicker to accelerate and smoother to drive because they don't have changing gears. Finally, EVs can be conveniently charged without expensive petrol stations.What is the economic potential of the Electric Vehicle market in India?
India sells many vehicles every year combined, and the government has ambitious targets for 2030. As a result, the total addressable market for new vehicles in 2030 encompasses almost 15 million vehicles. This bright future of electric vehicles in India offers a huge chance for vehicle manufacturers. Its also an opportunity for anyone looking to participate in this booming market.Resources
Bureau of Energy Efficiency: E-Mobility
Learn more about the general E-Mobility space from theMinistry of Power.
E-Amrit: Accelerated E-Mobility Revolution for India's Transportation
Seewhat the government is doingto support the transition to electric vehicles in India.
SECTION 80EEB: Tax Deductions
Find outwhich tax deductions are availablefor electric cars in India.
Bolt.Earth: Official Website
Get to know Bolt.Earth's products and services on ourofficial website.