Upgrading Your Home Garage for Safe and Efficient Electric Vehicle Charging

How Do I Prep My Garage for an EV?
You'll want a dedicated 240-volt circuit for charging your car. A professional installation generally runs between $750 and $1750, plus the price of permits, according to Qmerit, a company that specializes in this kind of work. If your current electrical supply can't handle the extra load, you'll need a new service line run to your house, pushing your cost to the high end of that range. A modest house with 150-amp or higher service can perhaps squeeze in an additional 30- or 40-amp circuit, but it depends on whether there are other large draws, such as a tankless water heater, an electric stove or dryer, or a hot tub. In addition, you may have to purchase charging equipment to connect your EV to the new circuit.

Wiring
The distance from the electrical panel to the charging location can alter the cost substantially. A 40-amp circuit requires 8-gauge wire at more than $3 per foot. Stepping up the amperage for faster charging requires thicker-gauge wire, which costs more.
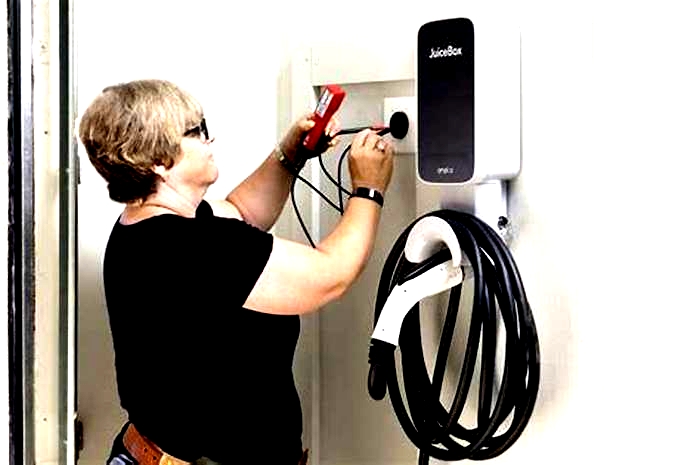
JuiceBox JuiceBox 40 Smart Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Station with Wi-Fi
JuiceBox JuiceBox 40 Smart Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Station with Wi-Fi
Outlet
We recommend installing a NEMA 14-50 outlet rather than hardwired charging equipment. Some EVs come with portable charging cords that work on both 120- and 240-volt circuits, saving you from an additional purchase. And even if you do buy home charging equipment, having a plug-in unit means you can use the outlet for other high-draw equipment, such as a welder, and take the pricey box with you if you move.
Equipment
Because we're nerds, we like to know how much energy our EVs are using. The Wi-Fi-connected JuiceBox ($650) has a handy app to track charging history and the amount of energy dispensed during each session. You can also schedule charging for set timesa useful feature if your electric utility offers a lower rate during off-peak hours.
Dave VanderWerp has spent more than 20 years in the automotive industry, in varied roles from engineering to product consulting, and now leading Car and Driver's vehicle-testing efforts. Dave got his very lucky start at C/D by happening to submit an unsolicited resume at just the right time to land a part-time road warrior job when he was a student at the University of Michigan, where he immediately became enthralled with the world of automotive journalism.
A Beginners Guide to Electric Cars: How to charge an EV at home
A Beginners Guide to Electric Cars: How to charge an EV at home
Most EV charging is done at home. After all, it is the most affordable and convenient way to charge an electric car. Find out everything you need to know about charging an electric vehicle at home in this quick guide.
It doesnt matter if your electric car is small or big, new or used, American, Japanese or South Korean, red, blue or purple. Every EV has a plug that you can use to charge at these locations:
That being said, electric car owners tend to mostly charge at home. In fact, most plug-in electric vehicle drivers do more than 80% of their charging at home (source: energy.gov). choose one for the majority of their EV charging sessions. Whether you live in a family home or an apartment, have a garage or private parking, charging your electric car at home is the most affordable and efficient way of charging your EVs battery.
Learn the simplicity of charging your electric car at home and youll learn how to magnify your benefits from driving electric.
Most plug-in electric vehicle drivers do more than 80% of their charging at home.
Electric Car Charging Speed: What you need to know
Have you ever used a household outlet to keep your gasoline car battery from dying when its freezing cold outside?
Yes? Did you know you can also charge your EV battery with the same outlet? In the world of electric vehicles, this type of charging is called level 1 charging. The charging station for this type of charging is usually supplied with the car. Therefore, all-electric vehicle owners have access to level 1 charging.
Now, we know what youre thinking: All I need to charge my EV at home is a household outlet? Easy peasy!
Just a moment! Theres more to know about electric car charging speed and how to use level 1 charging.
Although using a level 1 charging station is the most straightforward way to start charging your EV at home, it is generally only used for emergencies and roadside troubleshooting. Most of the time, it stays in the trunk of the vehicle. Heres why:
Level 1 charging stations are 120-volt plugs:
- It can take over 24 hours to deliver an optimal battery charge of 80% at a speed of about 9 km per hour (source: clippercreek.com).
- They can only charge one electric car at a time (the plug cannot be used by other appliances either).
A standard household outlet is what a Level 1 charging station plugs into.
You now understand that if you want to take advantage of a faster charging speed at home, you will need to equip yourself with a more efficient charging station.
The fastest way to charge your electric car at home is with a level 2 charging station. It can be installed on the side of your house, in a garage or your private parking lot. Also, it needs to be wired directly into your domestic electricity supply and may require a certified electrician to do so.
Level 2 charging stations have a 240-volt plug:
- It can deliver an optimal battery charge of 80% in 4 to 5 hours at a charging speed of about 22.5 km per hour for a plug-in hybrid and up to 45 km per hour for an all-electric vehicle (source: clippercreek.com).
- It is plugged into a special outlet or connected directly to the electrical panel.
A level 2 charging station is therefore a key element in truly enjoying all the advantages of charging at home: its practicality, ease of use, reliability and savings!
What about level 3 charging stations?
While faster charging stations exist, they cost thousands of dollars and have energy needs that surpass what is available in a home. As a result, they are currently only used for public charging. If youd like to learn more, check out our comprehensive guide to charging an electric car.
Equip your home with a Level 2 charging station
If you plan on charging your EV at home, the next key step is to equip your home with a level 2 charging station. These vary more and more in response to the increase of electric vehicle models available today. Youll consequently have to choose a charging station that best suits your needs and your lifestyle.
Some models are mounted to a wall, others are available as plug-in versions and can be moved. There are smart level 2 charging stations that allow you to view your charging history or even schedule charging sessions at specific times of the day. Some charging stations are better suited for cold weather than others.
Yes, there are many factors to consider when you decide to purchase a Level 2 charging station for your home. But fear not! The ChargeHub Team has prepared a guide on How to Choose Your Home Charging Station. Lets take a look, shall we?
How to Prepare Your Home and Garage for an Electric Vehicle
Electric vehicles are quiet, clean, and have a longer driving range than ever before. With zero tailpipe emissions, their carbon footprint is exponentially smaller than that of gas-consuming vehicles.
Electric vehicles are the future, too. California plans to implement a ban on the sale of gas vehicles by 2035 and more states and countries are sure to follow. So whether you already own one or plan to, it makes sense to prepare your home and garage for an electric vehicle.
Why You Need an EV Charger at Home
Public charging stations are one place to charge your electric vehicle (EV). Located streetside or in retail store parking lots, hotels, car dealerships, parking garages, or at your workplace, public charging stations extend your electric vehicle's reach.
When you're at home, you want your EV there, too. You need it for convenience, as well as for emergencies. It can take up to 12 hours to fully recharge an EV, so having an at-home charging option is ideal for most people.
Tip
If you want to charge your EV at home, you're not alone. The availability and performance of public charging stations can be spotty. So, over 90-percent of EV drivers say that they want to be able to charge their vehicles at home, according to the most recent survey of consumers.
Charging your EV at home means reliable charging when you want it, without having to compete with other drivers for public charging stations. You'll also pay a predictable electricity rate, through your home utility bill, rather than paying rates and surcharges set by the public charger.
How EV Chargers Work
Electric vehicles receive electricity from EVSE (electric vehicle service equipment), commonly known as an electric vehicle charging station. The EVSE receives its power from the home's electrical system.
Home-based EV charging stations technically are not chargers. Electric vehicles have chargers built into them. These onboard chargers receive the Alternating Current (AC) current from your home and convert it to Direct Current (DC) power for the car's battery pack.
To charge your electric vehicle at home, you have two options: a slower Level 1 charger that runs off of a regular 120 V outlet and a faster Level 2 charger that uses 240/208 V power. One reason commercial-grade chargers are faster than home chargers is because they bypass the onboard vehicle charger and provide DC power directly to the car's battery.
Types of Electric Vehicle Chargers
| Level 1 | Level 2 | |
| Charging Rate | Slow | Faster |
| Range Per Hour of Charging | 2 to 5 miles per charging hour | 10 to 20 miles per charging hour |
| Voltage | 120 V | 240/208 V |
| Home Installation | Outlet is usually already available | Outlet typically needs to be installed |
| Cost Including Install | $0 to $600 | $500 to $4,800 |
| Vehicle Plug Type | J1772 | J1772 |
Level 1 EV Chargers
With a Level 1 charger, one end of the cable plugs into your electric vehicle's charge port. The other end plugs into an ordinary home 120 V outlet.
A Level 1 charger comes as part of most EV packages, so there is nothing extra that you need to purchase. Most garages already have a 120 V outlet. If one needs to be installed, the cost ranges from $130 to $300.
Level 1 chargers are the slowest type of EV charger, charging at a rate of about 2 to 5 miles per hour.
A short overnight charge of eight hours takes the vehicle to 40 miles. A 12-hour charge gives the vehicle a 60-mile range. Since most U.S. work commutes are less than 30 minutes one-way, that's sufficient to get to work and back, even without a mid-day charge.
Level 2 EV Chargers
With a Level 2 charger, one end of the cable plugs into the electric vehicle's charge port. The other end is hardwired into the home's pre-installed EVSE wall station. The EVSE is powered by a 240/208 V outlet. In some cases, the other end of the cord plugs directly into the 240 V outlet, minus the wall station.
Level 2 EV chargers charge at a rate of about 10 to 20 miles per hour. That's more than enough to charge up for the following day at work. Given that the median range for most EVs is over 250 miles, 10 hours on a Level 2 charger is enough for most trips.
Most EVs use a J1172 or J-plug for Level 2 charging; Tesla doesn't have this direct option, but it does sell a J1772 and CHAdeM0 adaptor, which can cost from $150 to $200.
A Level 2 EV charger requires either a hardwired electrical connection or a NEMA 14-50 outlet on a dedicated circuit. Many EV chargers up to 40 A service utilize the plug-in connection type and can be installed by the homeowner.
What About Level 3 DC Fast Chargers?
Using 480 V power, DC Fast Chargers can charge up an EV at a rate that adds up to 10 miles more per minute of charging time. Infrastructure challenges still make residential Level 3 charging impossible.
EV Charger Costs
For Level 1 electric vehicle charging, the cost to install a charging station ranges from free to around $300. Most garages already have a 120 V outlet installed. If not, a qualified electrician can install one for up to $300. If you are handy, you can install your own 120 V outlet for less than $50.
For Level 2 EV charging at home, expect to pay at least $1,500 to $1,800 for a bundled package, including the charger and electrical installation.
A 240 V, 40 A Level 2 EV charging station, attached to a NEMA 14-50 outlet with a 20-foot cord J1772 cable, starts at about $200 to $400. This type of charging station is not Wi-Fi-equipped and it has no permanent wall station. Models with Wi-Fi and a wall-mounted station cost from $500 to $800.
Garage Space Considerations
The electric vehicle charger should preferably be installed on the same side of the vehicle's charge port and as close as possible.
- Place the EV charger within 15 to 20 feet of the vehicle's charge port. EV cords can be as long as 25 feet, with 18 to 20 feet being the norm.
- The EV charger and the 240 V outlet should be within about 3 to 4 feet of each other.
- The charger should be at least 18 inches off of the garage floor, preferably between 42 and 48 inches high.
- Make sure that the charger is within range of your home's local Wi-Fi network or is able to access cellular communications.
- For two EVs in the same two-car garage, mount the EV charger on a wall between the two vehicles for equal access by both vehicles.
Safety Considerations
Unless you are experienced at working inside electric service panels and adding circuits, it's usually best to have an electrician add the 240 V outlet.
Contact an experienced electrician if you want to hardwire the EV charger. Hardwiring means that you wire the charger directly into the electrical system rather than plugging it into a 240 V outlet.
How to Install an EV Charger
For Level 1 EV charging, simply connect the cord provided by the vehicle manufacturer to a 120 V wall outlet in the garage. For Level 2 EV charging, install a 240 V outlet near the intended location of the EVSE.
Apply For Permits
To install a 240 V outlet in the garage or on the side of the house, first obtain a permit from your local permitting office. A plan review may be required.
A double circuit breaker configuration needs to be installed in two adjacent open slots of the electric service panel. After installing the circuit breakers, turn the breakers to the OFF position.
Run Electric Cable to EV Charger Location
For 32 A or 40 A service, install 8 AWG cable to the circuit breaker. The cable can be hidden in the walls and ceiling of the garage. If the cable will be exposed on the surfaces, it must be contained within metal or PVC conduit.
Tip
For increased 48 A service, use the thicker 6 AWG cable. EVSEs in the 48 A and greater range may not have a plug-in option and must be hardwired only.
Install 240 V Outlet
Install the 240 V outlet within a few feet of the intended charger location.
Attach Mounting Bracket to the Stud
Attach the electric vehicle charger's mounting bracket directly to a stud on the garage wall.
Turn on EVSE
Plug the wall station into the outlet. Turn on the double circuit breakers on the electric service panel.
Attach Cable Holder (Optional)
Some EV chargers have a cable holder that must be installed separately. Other chargers may have a built-in cable holder.
FAQ
A Level 2 EV charger costs from $1,500 to $1,800, including installation and materials. Homeowners may may lower or much higher depending on several factors.
The best way to prepare your garage for an electric car is to clear one side of the garage as a dedicated space for the vehicle. At a minimum, this side should have direct access to a 120 V outlet for slow charging. Preferably, it should be close to the electric service panel for the installation of a 240 V outlet for faster Level 2 charging.
Most electric vehicles come with a Level 1 EV charger that can be plugged into 120 V outlets. Most EVs do not come with Level 2 chargers.
Bi-directional charging, where an electric vehicle powers the home in the event of a blackout, is still in its early stages. For now, you cannot run your house off of your electric vehicle. In fact, some areas, like California, expressly prohibit backfeeding a house from an electric vehicle.
The Spruce uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles. Read our
editorial processto learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy.