What are the disadvantages of a hybrid car

Pros and Cons of Hybrid cars
Whats good about hybrid carsAnd whats notThe key points of interest in 2023
Electric cars may be the future, but thebest hybrid carsrepresent a useful stepping-stone for many. Whether youre in the market for aplug-in hybrid,mild-hybridor aself-charging hybrid a hybrid car comes with a range of useful benefits over a petrol or diesel car and even an electric car. However, like any form of technology, hybrid cars also come with pros and cons you ought to consider before making a decision.
On this page, well outline the pros and cons of hybrid cars; from the highs of improved fuel economy to the lows of increased costs.

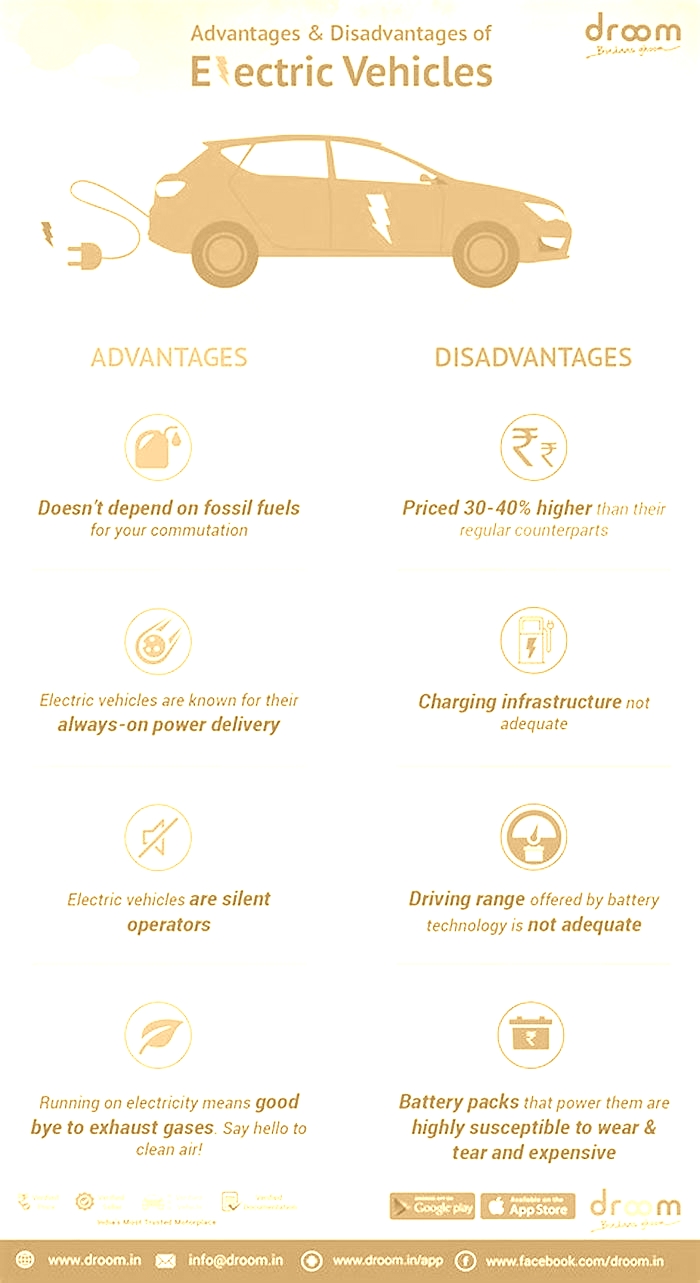
Advantages of hybrid cars
1. Improved fuel economy
Some hybrids use a combination of electricity and fossil fuel to improve performance, but most use their electric power to increase efficiency. Hybrids can save fuel by using solely electric power at low speeds around town, and they can also use electric motors to aid the internal combustion engine under harder acceleration. Both reduce the amount of fossil fuel used.
Hybrid cars can retrieve energy too. When braking, hybrid cars can recooperate kinetic energy, and return it to the battery as electricity. This energy is usually lost in conventional ICE-powered cars, and its another way hybrid cars can save energy and money. Take theToyota Corollafor instance; featuring a mpg figure of 62.8, its one of the thriftiest cars you can buy.

2. Cheaper running costs
Regenerative braking (described above) relies on resistance from the powertrain in combination with traditional braking systems. As a result, the braking systems on hybrid cars tend to be under less demand, and therefore consume brake pads at a slower rate than their ICE counterparts. Add that to the fuel savings, and hybrid cars can be considerably cheaper to maintain in the long run.

3. Better for the environment
Hybrid cars may use a petrol or diesel engine, but theyre still much cleaner to run than a purely fossil fuel-powered car. For example, the hugely popularBMW 330ecan achieve up to 138mpg, with 39g/km CO2. Compare that to the standard car, which can achieve 51.4mpg and 127-145g/km of CO2 in diesel form.
4. No range anxiety
Electric cars may come with several benefits, but they suffer from a reduced range compared to their fossil-fuel counterparts. And when things do run out, theyre harder to recharge on the go than a conventional car.In contrast, hybrid cars use electricity exclusively, but can easily switch to petrol or diesel power if the battery is empty. This provides increased peace of mind, especially in areas with a patchy charging network.
The presence of an ICE also means that hybrid cars and particularly self-charging cars can provide a very similar owning experience to conventionally powered cars.

5. Better performance around town
Although hybrid cars tend to be geared around efficiency rather than performance, their electric motors mean they can be extremely responsive at lower speeds. If you need a car thats good off the lights and nippy within the city limits, a hybrid could be a good choice.
The disadvantages of hybrid cars
1. More expensive than ICE cars
Hybrid cars may come with savings in the long run, but youll need to pay more for them in the short-term. Rare earth metals and lithium-ion batteries dont come cheap, and nor does the hybrid technology that surrounds them. For that reason, expect to pay a premium if youre buying new or second hand, and dont expect the government to help either the government grant for hybrid cars has been scrapped.
2. Battery expectancy
Just like the batteries in our mobile phones and laptops, the batteries in hybrid and electric cars can deteriorate over time. Battery capacity and performance may be reduced depending on the usage or age of the vehicle, and it may mean shorter periods between charges.

3. Hybrids still need to be charged
Hybrids can run without on petrol or diesel if theres no electric power, but that doesnt mean you should neglect charging them. If a hybrid car is left uncharged itll significantly less economical than a conventional ICE-powered car: Battery and hybrid tech is heavy, and dragging it around without any of its benefits will see a big reduction in your mpg figures.
4. Hybrid cars arent as good for the planet
Hybrid cars may be cheaper to run and kinder to the planet than conventionally powered cars, but they still use an internal combustion engine. That means they still produce CO2 and other emissions like petrol or diesel cars just less of them.
CarBuzz
Hybrid cars are becoming increasingly popular, and they can be an excellent intermediate step for those who want to explore electrification without buying a fully electric vehicle yet. With several types of hybrid car available, from mild hybrid to plug-in hybrid, there is a wide variety of choices available no matter what your lifestyle and driving needs.
But what are the pros and cons of hybrids? When does a hybrid suit your lifestyle, and when is it simply unnecessary? To answer these questions, we first need to understand the basics of hybrids.
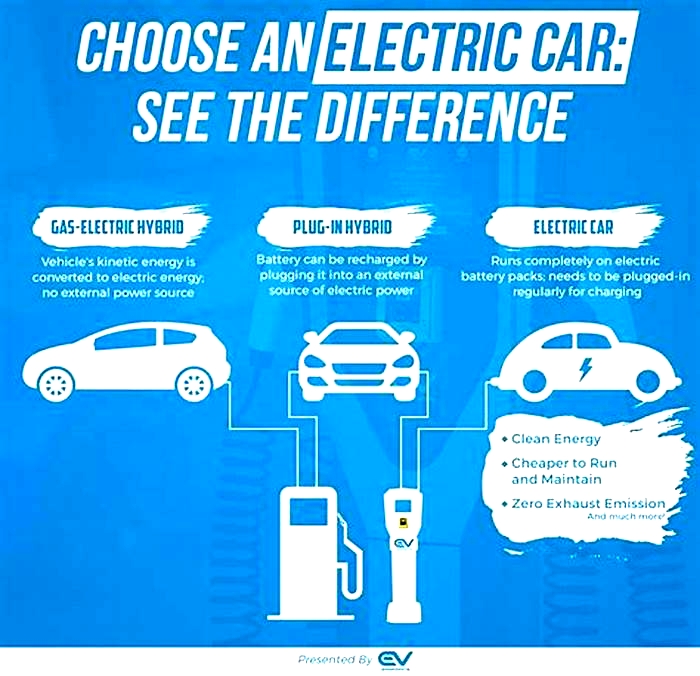
Types of Hybrid Vehicles
There are three main varieties of hybrid cars currently available on the market:
- Mild hybrid cars are the newest type of hybrid on the market and are rapidly gaining in popularity due to the fact that many cars you don't think of as hybrids use this type of powertrain. The BMW M340i, for example, supports its inline six with mild hybrid propulsion. Their main source of power is their traditional internal combustion engine. The electric motor (which has a battery charged via regenerative braking and does not need plugging in) exclusively serves the purpose of improving fuel economy by assisting in pulling away from a standstill, coasting, and using the 48-volt hybrid system to power ancillaries (air-con, infotainment, etc) and remove this load from the combustion engine. A mild hybrid vehicle is as close as you can get to a traditional ICE car while still enjoying the improved fuel economy of a hybrid, so you get the best of both worlds.
- Full (self-charging) hybrids also use regenerative braking to charge the electric motor, but unlike a mild hybrid, they can drive for a short distance on electric power alone, which makes them an ideal candidate for a prospective buyer with a short, city-based commute. The regular Toyota Prius is an example of this type of hybrid.
- Plug-in hybrids, as their name suggests, can be plugged into an external electric power source and charged to function as a hybrid, but they can also utilize regenerative braking, coasting, and charging via ICE. Thanks to their larger battery, they have the ability to utilize for full-electric-mode driving.
Some Pros And Cons Of Hybrids
Like any other type of vehicle, hybrid cars also have some drawbacks; despite being hyped as the optimal choice to future-proof your garage, a hybrid car may not be well suited for everyone. Here are some pros and cons of hybrid vehicles that will help you decide on your next purchase:
PRO: Better Fuel Economy and Lower Running Costs
The first thing that comes to mind when thinking about the advantages of choosing a hybrid car is fuel savings. With fuel costs rising, for many prospective car buyers, having a fuel-efficient vehicle is high on the list of priorities. Thanks to the presence of the battery providing better fuel efficiency than you'd normally find in traditional gas-powered cars, a self-charging hybrid (such as the Toyota Corolla Hybrid) can easily achieve 50 mpg, and a plug-in hybrid (such as the Hyundai Tucson PHEV) can push that figure up to 80 MPGe. This is especially true if you have a short, city-based commute at low speeds since many hybrid vehicles are capable of fully electric driving for shorter trips, making your car even more fuel-efficient overall.
CON: More Expensive Up-Front Than Traditional, Gas-Powered Cars
The running and fueling costs of a hybrid vehicle may be lower than those of a conventional car, but there almost definitely will be a higher upfront cost. Even a used hybrid car will typically cost more than its internal combustion engine-only counterparts, thanks to the high cost of the rare metals needed for battery technology. Thankfully, this higher upfront cost will likely be offset after a few years of ownership since you'll save money in the long run when it comes to fuel and maintenance.
This will change as hybrid cars proliferate automakers' lineups as the default option, and like all technology, the more widely it becomes available, the more affordable it becomes.
PRO: Avoid EV Range Anxiety
The range anxiety issue that typically plagues electric car users is eliminated when driving a hybrid vehicle: no matter what your driving habits, from work commutes to long-distance road trips, you can always rely on being able to fill up your car with gas as you would do with conventional cars. Plug-in hybrids even give you the best of both worlds. If you live within a short commute of work, you can easily live an EV lifestyle, relying only on gas when you aren't able to charge or need to drive long distances.
CON: Needs Both Charging and Refueling
Of course, when away from home, filling up at a gas station will get you from A to B in a pinch, but for everyday use, it is important not to neglect the charging aspect; if the battery in a plug-in hybrid is left uncharged, the benefit of higher fuel efficiency is negated, and the vehicle becomes a heavier, less efficient gas-powered car, often with hampered performance. This has become prevalent where buyers have bought PHEVs for the tax benefits and driven them around on gas power alone.
PRO: Well Suited to City Driving
If your driving habits typically involve short city journeys, then a hybrid could be the perfect choice for you: with its potential for all-electric driving, lower tailpipe emissions, and lower maintenance costs hybrids can make excellent city runabouts. At low speeds and with low throttle loads, the electric motors handle most of your propulsion needs. Combustion cars typically at their least efficient when idling and creeping in traffic, and it's in these circumstances that a hybrid excels, switching off the combustion engine and using its electric reserves.
CON: Less Effective on Long-Distance Journeys
Long-distance drivers, on the other hand, might struggle more with hybrid ownership. Hybrids are not always aimed at being more efficient at higher speeds, so their benefit at highway speeds is often entirely negated. We won't say they're worse than a non-hybrid, but the price you pay may not be rewarded if this is the type of driving you do the most.
PRO: Performance Benefits
Hybrids are traditionally seen as environmentally friendly, often assumed to mean reduced performance. However, the addition of electrical augmentation actually means the potential for enhanced performance. Electricity produces more efficient horsepower and greater torque than a combustion motor right from a single rpm. Electric motors can be used as torque-fill to mitigate turbo lag and enhance performance when the torque from a combustion motor is weak. The new Toyota Prus, for example, is as quick in a straight line as a GR86.
CON: Battery Life Expectancy
All batteries lose capacity and start to degrade with regular use, and the battery pack of a hybrid car is no exception: if you have owned your car for a few years or bought a used vehicle, you may start noticing the battery lasting less and less in between charges. Battery tech is getting better, and long manufacturer warranties do ensure replacement in most circumstances, but as more hybrids populate the used car market, this is still something to be aware of.
Outside of warranty, replacement batteries are notoriously expensive. The upside is that a hybrid can still operate as a normal gas car when the battery is no longer effective, meaning it isn't bricked entirely.
PRO: Less Maintenance Needed
Battery replacements aside, hybrid cars may require less day-to-day maintenance than conventional vehicles: in a car with a regenerative braking system, the brake pads will usually wear down at a lower rate, requiring less frequent replacement. The engines often strain less, too, and runs less per 100 miles when electric driving is a factor, again reducing wear.
CON: Higher Repair Costs
The routine maintenance of a hybrid car is slightly different from that of a conventional ICE-only vehicle, and not all mechanics specialize in hybrid cars. While typical maintenance of the engine remains unchanged, and the battery and electric motors don't require a lot of maintenance in general, when something goes wrong with the hybrid systems, a regular mechanic may not be able to do what needs to be done. In these instances, higher repair costs due to specialist workshops are a reality, or at least workshops where mechanics have undergone hybrid-specific training.
PRO: Lower Emissions
And lastly, onto the environmental aspect: with the aid of electric power and more efficient fuel consumption, hybrids will almost always produce lower tailpipe emissions than exclusively gas-powered cars, so if emissions are an important factor to you, a hybrid car might just be the right choice.
CON: Still Uses Gas
Whether you're an electric evangelist or a combustion die-hard, the science is impossible to refute that an electric vehicle is a far more efficient means of propulsion than burning gasoline to power the wheels. While there is no such thing as a zero-emissions vehicle, hybrid vehicles get closer to that mark. Still, they are not as efficient as electric cars, and for some people, the concept of still using gas is a big no. However, because of their smaller batteries, an argument could be made that they have a lesser environmental impact at a supply chain level.
Yeah, we'll admit this isn't the strongest con out there, but for some, any gas at all is a negative.